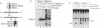Abstract
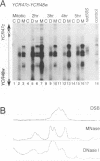
We have determined the precise location and structure of the double-strand DNA breaks (DSBs) formed during Saccharomyces cerevisiae meiosis. Breaks were examined at two recombination hot spots in both wild-type and rad50S mutant cells. At both loci, breaks occurred at multiple, irregularly spaced sites in a approximately 150 nucleotide interval contained within an area of nuclease-hypersensitive chromatin. No consensus sequence could be discerned at or around break sites. Patterns of cleavage observed on individual strands indicated that breaks initially form with a two nucleotide 5' overhang. Broken strands from rad50S mutant cells contained tightly bound protein at their 5' ends. We suggest that, in S.cerevisiae, meiotic recombination is initiated by a DSB-forming activity that creates a covalently linked protein-DNA intermediate.
Full text
PDF









Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alani E., Padmore R., Kleckner N. Analysis of wild-type and rad50 mutants of yeast suggests an intimate relationship between meiotic chromosome synapsis and recombination. Cell. 1990 May 4;61(3):419–436. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90524-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andersen A. H., Svejstrup J. Q., Westergaard O. The DNA binding, cleavage, and religation reactions of eukaryotic topoisomerases I and II. Adv Pharmacol. 1994;29A:83–101. doi: 10.1016/s1054-3589(08)60541-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop D. K., Park D., Xu L., Kleckner N. DMC1: a meiosis-specific yeast homolog of E. coli recA required for recombination, synaptonemal complex formation, and cell cycle progression. Cell. 1992 May 1;69(3):439–456. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90446-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cao L., Alani E., Kleckner N. A pathway for generation and processing of double-strand breaks during meiotic recombination in S. cerevisiae. Cell. 1990 Jun 15;61(6):1089–1101. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90072-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Church G. M., Gilbert W. Genomic sequencing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(7):1991–1995. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.7.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark J. M. Novel non-templated nucleotide addition reactions catalyzed by procaryotic and eucaryotic DNA polymerases. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Oct 25;16(20):9677–9686. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.20.9677. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cool M., Malone R. E. Molecular and genetic analysis of the yeast early meiotic recombination genes REC102 and REC107/MER2. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Mar;12(3):1248–1256. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.3.1248. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dujon B., Belfort M., Butow R. A., Jacq C., Lemieux C., Perlman P. S., Vogt V. M. Mobile introns: definition of terms and recommended nomenclature. Gene. 1989 Oct 15;82(1):115–118. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(89)90035-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebeling W., Hennrich N., Klockow M., Metz H., Orth H. D., Lang H. Proteinase K from Tritirachium album Limber. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Aug 15;47(1):91–97. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03671.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engebrecht J. A., Voelkel-Meiman K., Roeder G. S. Meiosis-specific RNA splicing in yeast. Cell. 1991 Sep 20;66(6):1257–1268. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90047-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fan Q., Xu F., Petes T. D. Meiosis-specific double-strand DNA breaks at the HIS4 recombination hot spot in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae: control in cis and trans. Mol Cell Biol. 1995 Mar;15(3):1679–1688. doi: 10.1128/mcb.15.3.1679. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galbraith A. M., Malone R. E. Characterization of REC104, a gene required for early meiotic recombination in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Dev Genet. 1992;13(6):392–402. doi: 10.1002/dvg.1020130603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Game J. C. Pulsed-field gel analysis of the pattern of DNA double-strand breaks in the Saccharomyces genome during meiosis. Dev Genet. 1992;13(6):485–497. doi: 10.1002/dvg.1020130610. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gimble F. S., Thorner J. Purification and characterization of VDE, a site-specific endonuclease from the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Biol Chem. 1993 Oct 15;268(29):21844–21853. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldway M., Sherman A., Zenvirth D., Arbel T., Simchen G. A short chromosomal region with major roles in yeast chromosome III meiotic disjunction, recombination and double strand breaks. Genetics. 1993 Feb;133(2):159–169. doi: 10.1093/genetics/133.2.159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goyon C., Lichten M. Timing of molecular events in meiosis in Saccharomyces cerevisiae: stable heteroduplex DNA is formed late in meiotic prophase. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Jan;13(1):373–382. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.1.373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haber J. E., Ray B. L., Kolb J. M., White C. I. Rapid kinetics of mismatch repair of heteroduplex DNA that is formed during recombination in yeast. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Apr 15;90(8):3363–3367. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.8.3363. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ivanov E. L., Korolev V. G., Fabre F. XRS2, a DNA repair gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae, is needed for meiotic recombination. Genetics. 1992 Nov;132(3):651–664. doi: 10.1093/genetics/132.3.651. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kane S. M., Roth R. Carbohydrate metabolism during ascospore development in yeast. J Bacteriol. 1974 Apr;118(1):8–14. doi: 10.1128/jb.118.1.8-14.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kostriken R., Strathern J. N., Klar A. J., Hicks J. B., Heffron F. A site-specific endonuclease essential for mating-type switching in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Cell. 1983 Nov;35(1):167–174. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90219-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lichten M., Goyon C., Schultes N. P., Treco D., Szostak J. W., Haber J. E., Nicolas A. Detection of heteroduplex DNA molecules among the products of Saccharomyces cerevisiae meiosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Oct;87(19):7653–7657. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.19.7653. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Little J. W. An exonuclease induced by bacteriophage lambda. II. Nature of the enzymatic reaction. J Biol Chem. 1967 Feb 25;242(4):679–686. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malone R. E., Bullard S., Hermiston M., Rieger R., Cool M., Galbraith A. Isolation of mutants defective in early steps of meiotic recombination in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics. 1991 May;128(1):79–88. doi: 10.1093/genetics/128.1.79. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Menees T. M., Ross-MacDonald P. B., Roeder G. S. MEI4, a meiosis-specific yeast gene required for chromosome synapsis. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Mar;12(3):1340–1351. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.3.1340. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nag D. K., Petes T. D. Physical detection of heteroduplexes during meiotic recombination in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Apr;13(4):2324–2331. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.4.2324. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicolas A., Treco D., Schultes N. P., Szostak J. W. An initiation site for meiotic gene conversion in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Nature. 1989 Mar 2;338(6210):35–39. doi: 10.1038/338035a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohta K., Shibata T., Nicolas A. Changes in chromatin structure at recombination initiation sites during yeast meiosis. EMBO J. 1994 Dec 1;13(23):5754–5763. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06913.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliver S. G., van der Aart Q. J., Agostoni-Carbone M. L., Aigle M., Alberghina L., Alexandraki D., Antoine G., Anwar R., Ballesta J. P., Benit P. The complete DNA sequence of yeast chromosome III. Nature. 1992 May 7;357(6373):38–46. doi: 10.1038/357038a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Padmore R., Cao L., Kleckner N. Temporal comparison of recombination and synaptonemal complex formation during meiosis in S. cerevisiae. Cell. 1991 Sep 20;66(6):1239–1256. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90046-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pittman D., Lu W., Malone R. E. Genetic and molecular analysis of REC114, an early meiotic recombination gene in yeast. Curr Genet. 1993;23(4):295–304. doi: 10.1007/BF00310890. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porter S. E., White M. A., Petes T. D. Genetic evidence that the meiotic recombination hotspot at the HIS4 locus of Saccharomyces cerevisiae does not represent a site for a symmetrically processed double-strand break. Genetics. 1993 May;134(1):5–19. doi: 10.1093/genetics/134.1.5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ray B. L., White C. I., Haber J. E. Heteroduplex formation and mismatch repair of the "stuck" mutation during mating-type switching in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Oct;11(10):5372–5380. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.10.5372. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reece R. J., Maxwell A. DNA gyrase: structure and function. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 1991;26(3-4):335–375. doi: 10.3109/10409239109114072. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rocco V., de Massy B., Nicolas A. The Saccharomyces cerevisiae ARG4 initiator of meiotic gene conversion and its associated double-strand DNA breaks can be inhibited by transcriptional interference. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Dec 15;89(24):12068–12072. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.24.12068. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose D., Holm C. Meiosis-specific arrest revealed in DNA topoisomerase II mutants. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Jun;13(6):3445–3455. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.6.3445. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwacha A., Kleckner N. Identification of joint molecules that form frequently between homologs but rarely between sister chromatids during yeast meiosis. Cell. 1994 Jan 14;76(1):51–63. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90172-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimizu M., Roth S. Y., Szent-Gyorgyi C., Simpson R. T. Nucleosomes are positioned with base pair precision adjacent to the alpha 2 operator in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. EMBO J. 1991 Oct;10(10):3033–3041. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07854.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun H., Treco D., Schultes N. P., Szostak J. W. Double-strand breaks at an initiation site for meiotic gene conversion. Nature. 1989 Mar 2;338(6210):87–90. doi: 10.1038/338087a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun H., Treco D., Szostak J. W. Extensive 3'-overhanging, single-stranded DNA associated with the meiosis-specific double-strand breaks at the ARG4 recombination initiation site. Cell. 1991 Mar 22;64(6):1155–1161. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90270-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szostak J. W., Orr-Weaver T. L., Rothstein R. J., Stahl F. W. The double-strand-break repair model for recombination. Cell. 1983 May;33(1):25–35. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90331-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Udvardy A., Schedl P. Chromatin structure, not DNA sequence specificity, is the primary determinant of topoisomerase II sites of action in vivo. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Oct;11(10):4973–4984. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.10.4973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vincent R. D., Hofmann T. J., Zassenhaus H. P. Sequence and expression of NUC1, the gene encoding the mitochondrial nuclease in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Apr 25;16(8):3297–3312. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.8.3297. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White C. I., Haber J. E. Intermediates of recombination during mating type switching in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. EMBO J. 1990 Mar;9(3):663–673. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08158.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White M. A., Dominska M., Petes T. D. Transcription factors are required for the meiotic recombination hotspot at the HIS4 locus in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jul 15;90(14):6621–6625. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.14.6621. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu T. C., Lichten M. Factors that affect the location and frequency of meiosis-induced double-strand breaks in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics. 1995 May;140(1):55–66. doi: 10.1093/genetics/140.1.55. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu T. C., Lichten M. Meiosis-induced double-strand break sites determined by yeast chromatin structure. Science. 1994 Jan 28;263(5146):515–518. doi: 10.1126/science.8290959. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zassenhaus H. P., Denniger G. Analysis of the role of the NUC1 endo/exonuclease in yeast mitochondrial DNA recombination. Curr Genet. 1994 Feb;25(2):142–149. doi: 10.1007/BF00309540. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zenvirth D., Arbel T., Sherman A., Goldway M., Klein S., Simchen G. Multiple sites for double-strand breaks in whole meiotic chromosomes of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. EMBO J. 1992 Sep;11(9):3441–3447. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05423.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Massy B., Nicolas A. The control in cis of the position and the amount of the ARG4 meiotic double-strand break of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. EMBO J. 1993 Apr;12(4):1459–1466. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05789.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Massy B., Rocco V., Nicolas A. The nucleotide mapping of DNA double-strand breaks at the CYS3 initiation site of meiotic recombination in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. EMBO J. 1995 Sep 15;14(18):4589–4598. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1995.tb00138.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]