Abstract
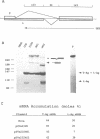
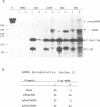
The influenza virus RNA segment 8 encodes two proteins, NS1 and NS2, by differential splicing. The collinear transcript acts as mRNA for NS1 protein, while the spliced mRNA encodes NS2 protein. The splicing of NS1 mRNA was studied in cells transfected with a recombinant plasmid that has the cDNA of RNA segment 8 cloned under the SV40 late promoter and polyadenylation signals. As described for influenza virus-infected cells, NS1 mRNA was poorly spliced to yield NS2 mRNA. However, inactivation of the NS1 gene, but not the NS2 gene, led to a substantial increase in the splicing efficiency, as shown by the relative accumulations of NS1 and NS2 mRNAs. This effect was not specific for NS1 mRNA, since the splicing of the endogenous SV40 early transcript was altered in such a way that t-Ag mRNA was almost eliminated. These changes in the splicing pattern coincided with a strong inhibition of the mRNA nucleocytoplasmic transport. Both NS1 and NS2 mRNAs were retained in the nucleus of cells expressing NS1 protein, but no effect was observed when only NS2 protein was expressed. Furthermore, other mRNAs tested, such as T-Ag mRNA and the non-spliceable nucleoprotein transcript, were also retained in the nucleus upon expression of NS1 protein, suggesting that it induced a generalized block of mRNA export from the nucleus.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Agris C. H., Nemeroff M. E., Krug R. M. A block in mammalian splicing occurring after formation of large complexes containing U1, U2, U4, U5, and U6 small nuclear ribonucleoproteins. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Jan;9(1):259–267. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.1.259. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alonso-Caplen F. V., Krug R. M. Regulation of the extent of splicing of influenza virus NS1 mRNA: role of the rates of splicing and of the nucleocytoplasmic transport of NS1 mRNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Feb;11(2):1092–1098. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.2.1092. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alonso-Caplen F. V., Nemeroff M. E., Qiu Y., Krug R. M. Nucleocytoplasmic transport: the influenza virus NS1 protein regulates the transport of spliced NS2 mRNA and its precursor NS1 mRNA. Genes Dev. 1992 Feb;6(2):255–267. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.2.255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amberg D. C., Fleischmann M., Stagljar I., Cole C. N., Aebi M. Nuclear PRP20 protein is required for mRNA export. EMBO J. 1993 Jan;12(1):233–241. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05649.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amberg D. C., Goldstein A. L., Cole C. N. Isolation and characterization of RAT1: an essential gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae required for the efficient nucleocytoplasmic trafficking of mRNA. Genes Dev. 1992 Jul;6(7):1173–1189. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.7.1173. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berk A. J., Sharp P. A. Spliced early mRNAs of simian virus 40. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Mar;75(3):1274–1278. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.3.1274. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braam J., Ulmanen I., Krug R. M. Molecular model of a eucaryotic transcription complex: functions and movements of influenza P proteins during capped RNA-primed transcription. Cell. 1983 Sep;34(2):609–618. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90393-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carmo-Fonseca M., Pepperkok R., Carvalho M. T., Lamond A. I. Transcription-dependent colocalization of the U1, U2, U4/U6, and U5 snRNPs in coiled bodies. J Cell Biol. 1992 Apr;117(1):1–14. doi: 10.1083/jcb.117.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carmo-Fonseca M., Pepperkok R., Sproat B. S., Ansorge W., Swanson M. S., Lamond A. I. In vivo detection of snRNP-rich organelles in the nuclei of mammalian cells. EMBO J. 1991 Jul;10(7):1863–1873. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07712.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carmo-Fonseca M., Tollervey D., Pepperkok R., Barabino S. M., Merdes A., Brunner C., Zamore P. D., Green M. R., Hurt E., Lamond A. I. Mammalian nuclei contain foci which are highly enriched in components of the pre-mRNA splicing machinery. EMBO J. 1991 Jan;10(1):195–206. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07936.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter K. C., Bowman D., Carrington W., Fogarty K., McNeil J. A., Fay F. S., Lawrence J. B. A three-dimensional view of precursor messenger RNA metabolism within the mammalian nucleus. Science. 1993 Feb 26;259(5099):1330–1335. doi: 10.1126/science.8446902. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter K. C., Taneja K. L., Lawrence J. B. Discrete nuclear domains of poly(A) RNA and their relationship to the functional organization of the nucleus. J Cell Biol. 1991 Dec;115(5):1191–1202. doi: 10.1083/jcb.115.5.1191. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dargemont C., Kühn L. C. Export of mRNA from microinjected nuclei of Xenopus laevis oocytes. J Cell Biol. 1992 Jul;118(1):1–9. doi: 10.1083/jcb.118.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fu X. D., Maniatis T. Factor required for mammalian spliceosome assembly is localized to discrete regions in the nucleus. Nature. 1990 Feb 1;343(6257):437–441. doi: 10.1038/343437a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ge H., Manley J. L. A protein factor, ASF, controls cell-specific alternative splicing of SV40 early pre-mRNA in vitro. Cell. 1990 Jul 13;62(1):25–34. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90236-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gluzman Y. SV40-transformed simian cells support the replication of early SV40 mutants. Cell. 1981 Jan;23(1):175–182. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90282-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanahan D. Studies on transformation of Escherichia coli with plasmids. J Mol Biol. 1983 Jun 5;166(4):557–580. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80284-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harper J. E., Manley J. L. A novel protein factor is required for use of distal alternative 5' splice sites in vitro. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Dec;11(12):5945–5953. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.12.5945. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatada E., Fukuda R. Binding of influenza A virus NS1 protein to dsRNA in vitro. J Gen Virol. 1992 Dec;73(Pt 12):3325–3329. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-73-12-3325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatada E., Takizawa T., Fukuda R. Specific binding of influenza A virus NS1 protein to the virus minus-sense RNA in vitro. J Gen Virol. 1992 Jan;73(Pt 1):17–25. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-73-1-17. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hozák P., Hassan A. B., Jackson D. A., Cook P. R. Visualization of replication factories attached to nucleoskeleton. Cell. 1993 Apr 23;73(2):361–373. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90235-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang S., Spector D. L. Nascent pre-mRNA transcripts are associated with nuclear regions enriched in splicing factors. Genes Dev. 1991 Dec;5(12A):2288–2302. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.12a.2288. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang T. S., Palese P., Krystal M. Determination of influenza virus proteins required for genome replication. J Virol. 1990 Nov;64(11):5669–5673. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.11.5669-5673.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson D. A., Caton A. J., McCready S. J., Cook P. R. Influenza virus RNA is synthesized at fixed sites in the nucleus. Nature. 1982 Mar 25;296(5855):366–368. doi: 10.1038/296366a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kadowaki T., Zhao Y., Tartakoff A. M. A conditional yeast mutant deficient in mRNA transport from nucleus to cytoplasm. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Mar 15;89(6):2312–2316. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.6.2312. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katze M. G., Krug R. M. Metabolism and expression of RNA polymerase II transcripts in influenza virus-infected cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Oct;4(10):2198–2206. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.10.2198. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koennecke I., Boschek C. B., Scholtissek C. Isolation and properties of a temperature-sensitive mutant (ts 412) of an influenza A virus recombinant with a ts lesion in the gene coding for the nonstructural protein. Virology. 1981 Apr 15;110(1):16–25. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90003-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krainer A. R., Conway G. C., Kozak D. Purification and characterization of pre-mRNA splicing factor SF2 from HeLa cells. Genes Dev. 1990 Jul;4(7):1158–1171. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.7.1158. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krainer A. R., Conway G. C., Kozak D. The essential pre-mRNA splicing factor SF2 influences 5' splice site selection by activating proximal sites. Cell. 1990 Jul 13;62(1):35–42. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90237-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamb R. A., Lai C. J., Choppin P. W. Sequences of mRNAs derived from genome RNA segment 7 of influenza virus: colinear and interrupted mRNAs code for overlapping proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jul;78(7):4170–4174. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.7.4170. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamb R. A., Lai C. J. Sequence of interrupted and uninterrupted mRNAs and cloned DNA coding for the two overlapping nonstructural proteins of influenza virus. Cell. 1980 Sep;21(2):475–485. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90484-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawrence J. B., Singer R. H., Marselle L. M. Highly localized tracks of specific transcripts within interphase nuclei visualized by in situ hybridization. Cell. 1989 May 5;57(3):493–502. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90924-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Legrain P., Rosbash M. Some cis- and trans-acting mutants for splicing target pre-mRNA to the cytoplasm. Cell. 1989 May 19;57(4):573–583. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90127-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- López-Turiso J. A., Martínez C., Tanaka T., Ortín J. The synthesis of influenza virus negative-strand RNA takes place in insoluble complexes present in the nuclear matrix fraction. Virus Res. 1990 Jul;16(3):325–337. doi: 10.1016/0168-1702(90)90056-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maquat L. E. Nuclear mRNA export. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1991 Dec;3(6):1004–1012. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(91)90121-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattaj I. W. Splicing stories and poly(A) tales: an update on RNA processing and transport. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1990 Jun;2(3):528–538. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(90)90138-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayeda A., Krainer A. R. Regulation of alternative pre-mRNA splicing by hnRNP A1 and splicing factor SF2. Cell. 1992 Jan 24;68(2):365–375. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90477-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melton D. A., Krieg P. A., Rebagliati M. R., Maniatis T., Zinn K., Green M. R. Efficient in vitro synthesis of biologically active RNA and RNA hybridization probes from plasmids containing a bacteriophage SP6 promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Sep 25;12(18):7035–7056. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.18.7035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munroe S. H., Dong X. F. Heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein A1 catalyzes RNA.RNA annealing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Feb 1;89(3):895–899. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.3.895. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nemeroff M. E., Utans U., Krämer A., Krug R. M. Identification of cis-acting intron and exon regions in influenza virus NS1 mRNA that inhibit splicing and cause the formation of aberrantly sedimenting presplicing complexes. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Mar;12(3):962–970. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.3.962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Odagiri T., Tobita K., Tashiro M. Synthesis of the NS 2 nonstructural protein messenger RNA of influenza A viruses occurs in the absence of viral protein synthesis. Arch Virol. 1991;120(3-4):281–288. doi: 10.1007/BF01310483. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ortin J., Doerfler W. Transcription of the genome of adenovirus type 12. I. Viral mRNA in abortively infected and transformed cells. J Virol. 1975 Jan;15(1):27–35. doi: 10.1128/jvi.15.1.27-35.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phi-Van L., von Kries J. P., Ostertag W., Strätling W. H. The chicken lysozyme 5' matrix attachment region increases transcription from a heterologous promoter in heterologous cells and dampens position effects on the expression of transfected genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 May;10(5):2302–2307. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.5.2302. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plumb M., Stein J., Stein G. Coordinate regulation of multiple histone mRNAs during the cell cycle in HeLa cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Apr 25;11(8):2391–2410. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.8.2391. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Portela A., Melero J. A., Martínez C., Domingo E., Ortín J. Oriented synthesis and cloning of influenza virus nucleoprotein cDNA that leads to its expression in mammalian cells. Virus Res. 1985 Dec;4(1):69–82. doi: 10.1016/0168-1702(85)90021-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Portela A., Melero J. A., de la Luna S., Ortín J. Construction of cell lines that regulate by temperature the amplification and expression of influenza virus non-structural protein genes. EMBO J. 1986 Sep;5(9):2387–2392. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04508.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raap A. K., van de Rijke F. M., Dirks R. W., Sol C. J., Boom R., van der Ploeg M. Bicolor fluorescence in situ hybridization to intron and exon mRNA sequences. Exp Cell Res. 1991 Dec;197(2):319–322. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(91)90439-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruby S. W., Abelson J. Pre-mRNA splicing in yeast. Trends Genet. 1991 Mar;7(3):79–85. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(91)90276-V. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santos T., Zasloff M. Comparative analysis of human chromosomal segments bearing nonallelic dispersed tRNAimet genes. Cell. 1981 Mar;23(3):699–709. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90433-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwer B., Guthrie C. PRP16 is an RNA-dependent ATPase that interacts transiently with the spliceosome. Nature. 1991 Feb 7;349(6309):494–499. doi: 10.1038/349494a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro G. I., Gurney T., Jr, Krug R. M. Influenza virus gene expression: control mechanisms at early and late times of infection and nuclear-cytoplasmic transport of virus-specific RNAs. J Virol. 1987 Mar;61(3):764–773. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.3.764-773.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimizu K., Mullinix M. G., Chanock R. M., Murphy B. R. Temperature-sensitive mutants of influenza A/Udorn/72 (H3N2) virus. I. Isolation of temperature-sensitive mutants some of which exhibit host-dependent temperature sensitivity. Virology. 1982 Feb;117(1):38–44. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(82)90505-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiokawa K., Pogo A. O. The role of cytoplasmic membranes in controlling the transport of nuclear messenger RNA and initiation of protein synthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Jul;71(7):2658–2662. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.7.2658. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. B., Inglis S. C. Regulated production of an influenza virus spliced mRNA mediated by virus-specific products. EMBO J. 1985 Sep;4(9):2313–2319. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03932.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spector D. L., Fu X. D., Maniatis T. Associations between distinct pre-mRNA splicing components and the cell nucleus. EMBO J. 1991 Nov;10(11):3467–3481. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb04911.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spector D. L. Higher order nuclear organization: three-dimensional distribution of small nuclear ribonucleoprotein particles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jan;87(1):147–151. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.1.147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. S. Hybridization of denatured RNA transferred or dotted nitrocellulose paper. Methods Enzymol. 1983;100:255–266. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)00060-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valcárcel J., Fortes P., Ortín J. Splicing of influenza virus matrix protein mRNA expressed from a simian virus 40 recombinant. J Gen Virol. 1993 Jul;74(Pt 7):1317–1326. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-74-7-1317. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valcárcel J., Portela A., Ortín J. Regulated M1 mRNA splicing in influenza virus-infected cells. J Gen Virol. 1991 Jun;72(Pt 6):1301–1308. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-72-6-1301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xing Y., Johnson C. V., Dobner P. R., Lawrence J. B. Higher level organization of individual gene transcription and RNA splicing. Science. 1993 Feb 26;259(5099):1326–1330. doi: 10.1126/science.8446901. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zahler A. M., Neugebauer K. M., Lane W. S., Roth M. B. Distinct functions of SR proteins in alternative pre-mRNA splicing. Science. 1993 Apr 9;260(5105):219–222. doi: 10.1126/science.8385799. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de la Luna S., Martín J., Portela A., Ortín J. Influenza virus naked RNA can be expressed upon transfection into cells co-expressing the three subunits of the polymerase and the nucleoprotein from simian virus 40 recombinant viruses. J Gen Virol. 1993 Mar;74(Pt 3):535–539. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-74-3-535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de la Luna S., Portela A., Martínez C., Ortín J. Permanent cell lines established from ts-COS cells that regulate by temperature the amplification and expression of cloned genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Aug 11;15(15):6117–6129. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.15.6117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]