Abstract
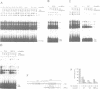
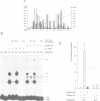
Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen 2 (EBNA-2) plays a crucial role in B cell immortalization by Epstein-Barr virus (EBV), most probably by its ability to transactivate several cellular and viral genes. Recently, we showed that EBNA-2 interacts with the TP1 promoter of EBV through a cellular protein. In this report we provide evidence that this protein is recombination signal binding protein (RBP)-J kappa, highly conserved in evolution, and originally isolated by its ability to bind to the J kappa-type V(D)J recombination signal sequence. To identify the cellular protein interacting with the TP1 promoter, we performed electrophoretic mobility shift assays using binding sequences of known transcription factors, that carry partial homology to the crucial sequences of the EBNA-2 responsive element (EBNA-2RE), as competitor. Competition assays revealed the RBP-J kappa recognition site as a very efficient competitor of cellular TP1 promoter binding protein. In parallel, we purified the protein to homogeneity from Raji cells by two ion-exchange columns and affinity purification using the EBNA-2RE coupled to magnetic beads. Affinity purified fractions separated on SDS-PAGE revealed a single predominant band after silver staining which was recognized by anti-RBP-J kappa monoclonal antibody. These purified fractions exhibited binding specificity for EBNA-2RE and EBNA-2. In vitro-translated murine RBP-2 cDNA reacted with EBNA-2RE and EBNA-2 in the same fashion as the affinity purified protein. The interaction between RBP-J kappa and EBNA-2 is a prerequisite for EBNA-2-mediated transactivation of the TP1 promoter.
Full text
PDF









Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allday M. J., Crawford D. H., Griffin B. E. Epstein-Barr virus latent gene expression during the initiation of B cell immortalization. J Gen Virol. 1989 Jul;70(Pt 7):1755–1764. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-70-7-1755. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baer R., Bankier A. T., Biggin M. D., Deininger P. L., Farrell P. J., Gibson T. J., Hatfull G., Hudson G. S., Satchwell S. C., Séguin C. DNA sequence and expression of the B95-8 Epstein-Barr virus genome. Nature. 1984 Jul 19;310(5974):207–211. doi: 10.1038/310207a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calender A., Billaud M., Aubry J. P., Banchereau J., Vuillaume M., Lenoir G. M. Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) induces expression of B-cell activation markers on in vitro infection of EBV-negative B-lymphoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Nov;84(22):8060–8064. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.22.8060. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen J. I., Wang F., Kieff E. Epstein-Barr virus nuclear protein 2 mutations define essential domains for transformation and transactivation. J Virol. 1991 May;65(5):2545–2554. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.5.2545-2554.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cordier M., Calender A., Billaud M., Zimber U., Rousselet G., Pavlish O., Banchereau J., Tursz T., Bornkamm G., Lenoir G. M. Stable transfection of Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) nuclear antigen 2 in lymphoma cells containing the EBV P3HR1 genome induces expression of B-cell activation molecules CD21 and CD23. J Virol. 1990 Mar;64(3):1002–1013. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.3.1002-1013.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crawford D. H., Epstein M. A., Bornkamm G. W., Achong B. G., Finerty S., Thompson J. L. Biological and biochemical observations on isolates of EB virus from the malignant epithelial cells of two nasopharyngeal carcinomas. Int J Cancer. 1979 Sep 15;24(3):294–302. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910240305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dou S., Zeng X., Cortes P., Erdjument-Bromage H., Tempst P., Honjo T., Vales L. D. The recombination signal sequence-binding protein RBP-2N functions as a transcriptional repressor. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 May;14(5):3310–3319. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.5.3310. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furukawa T., Maruyama S., Kawaichi M., Honjo T. The Drosophila homolog of the immunoglobulin recombination signal-binding protein regulates peripheral nervous system development. Cell. 1992 Jun 26;69(7):1191–1197. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90640-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fåhraeus R., Jansson A., Ricksten A., Sjöblom A., Rymo L. Epstein-Barr virus-encoded nuclear antigen 2 activates the viral latent membrane protein promoter by modulating the activity of a negative regulatory element. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Oct;87(19):7390–7394. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.19.7390. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gabrielsen O. S., Huet J. Magnetic DNA affinity purification of yeast transcription factor. Methods Enzymol. 1993;218:508–525. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(93)18038-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamaguchi Y., Matsunami N., Yamamoto Y., Honjo T. Purification and characterization of a protein that binds to the recombination signal sequence of the immunoglobulin J kappa segment. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Nov 25;17(22):9015–9026. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.22.9015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamaguchi Y., Yamamoto Y., Iwanari H., Maruyama S., Furukawa T., Matsunami N., Honjo T. Biochemical and immunological characterization of the DNA binding protein (RBP-J kappa) to mouse J kappa recombination signal sequence. J Biochem. 1992 Sep;112(3):314–320. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a123898. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hiebert S. W., Lipp M., Nevins J. R. E1A-dependent trans-activation of the human MYC promoter is mediated by the E2F factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 May;86(10):3594–3598. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.10.3594. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jin X. W., Speck S. H. Identification of critical cis elements involved in mediating Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen 2-dependent activity of an enhancer located upstream of the viral BamHI C promoter. J Virol. 1992 May;66(5):2846–2852. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.5.2846-2852.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawaichi M., Oka C., Shibayama S., Koromilas A. E., Matsunami N., Hamaguchi Y., Honjo T. Genomic organization of mouse J kappa recombination signal binding protein (RBP-J kappa) gene. J Biol Chem. 1992 Feb 25;267(6):4016–4022. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knutson J. C. The level of c-fgr RNA is increased by EBNA-2, an Epstein-Barr virus gene required for B-cell immortalization. J Virol. 1990 Jun;64(6):2530–2536. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.6.2530-2536.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lenardo M. J., Baltimore D. NF-kappa B: a pleiotropic mediator of inducible and tissue-specific gene control. Cell. 1989 Jul 28;58(2):227–229. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90833-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ling P. D., Rawlins D. R., Hayward S. D. The Epstein-Barr virus immortalizing protein EBNA-2 is targeted to DNA by a cellular enhancer-binding protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Oct 15;90(20):9237–9241. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.20.9237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsunami N., Hamaguchi Y., Yamamoto Y., Kuze K., Kangawa K., Matsuo H., Kawaichi M., Honjo T. A protein binding to the J kappa recombination sequence of immunoglobulin genes contains a sequence related to the integrase motif. Nature. 1989 Dec 21;342(6252):934–937. doi: 10.1038/342934a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mudryj M., Hiebert S. W., Nevins J. R. A role for the adenovirus inducible E2F transcription factor in a proliferation dependent signal transduction pathway. EMBO J. 1990 Jul;9(7):2179–2184. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07387.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nye J. A., Petersen J. M., Gunther C. V., Jonsen M. D., Graves B. J. Interaction of murine ets-1 with GGA-binding sites establishes the ETS domain as a new DNA-binding motif. Genes Dev. 1992 Jun;6(6):975–990. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.6.975. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PULVERTAFT J. V. A STUDY OF MALIGNANT TUMOURS IN NIGERIA BY SHORT-TERM TISSUE CULTURE. J Clin Pathol. 1965 May;18:261–273. doi: 10.1136/jcp.18.3.261. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddy E. S., Rao V. N. erg, an ets-related gene, codes for sequence-specific transcriptional activators. Oncogene. 1991 Dec;6(12):2285–2289. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ring C. J. The B cell-immortalizing functions of Epstein-Barr virus. J Gen Virol. 1994 Jan;75(Pt 1):1–13. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-75-1-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rooney C., Howe J. G., Speck S. H., Miller G. Influence of Burkitt's lymphoma and primary B cells on latent gene expression by the nonimmortalizing P3J-HR-1 strain of Epstein-Barr virus. J Virol. 1989 Apr;63(4):1531–1539. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.4.1531-1539.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schweisguth F., Posakony J. W. Suppressor of Hairless, the Drosophila homolog of the mouse recombination signal-binding protein gene, controls sensory organ cell fates. Cell. 1992 Jun 26;69(7):1199–1212. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90641-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sung N. S., Kenney S., Gutsch D., Pagano J. S. EBNA-2 transactivates a lymphoid-specific enhancer in the BamHI C promoter of Epstein-Barr virus. J Virol. 1991 May;65(5):2164–2169. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.5.2164-2169.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson C. B., Wang C. Y., Ho I. C., Bohjanen P. R., Petryniak B., June C. H., Miesfeldt S., Zhang L., Nabel G. J., Karpinski B. cis-acting sequences required for inducible interleukin-2 enhancer function bind a novel Ets-related protein, Elf-1. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Mar;12(3):1043–1053. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.3.1043. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsang S. F., Wang F., Izumi K. M., Kieff E. Delineation of the cis-acting element mediating EBNA-2 transactivation of latent infection membrane protein expression. J Virol. 1991 Dec;65(12):6765–6771. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.12.6765-6771.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tun T., Hamaguchi Y., Matsunami N., Furukawa T., Honjo T., Kawaichi M. Recognition sequence of a highly conserved DNA binding protein RBP-J kappa. Nucleic Acids Res. 1994 Mar 25;22(6):965–971. doi: 10.1093/nar/22.6.965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang F., Gregory C. D., Rowe M., Rickinson A. B., Wang D., Birkenbach M., Kikutani H., Kishimoto T., Kieff E. Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen 2 specifically induces expression of the B-cell activation antigen CD23. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 May;84(10):3452–3456. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.10.3452. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang F., Kikutani H., Tsang S. F., Kishimoto T., Kieff E. Epstein-Barr virus nuclear protein 2 transactivates a cis-acting CD23 DNA element. J Virol. 1991 Aug;65(8):4101–4106. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.8.4101-4106.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasylyk B., Hahn S. L., Giovane A. The Ets family of transcription factors. Eur J Biochem. 1993 Jan 15;211(1-2):7–18. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-78757-7_2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimber-Strobl U., Kremmer E., Grässer F., Marschall G., Laux G., Bornkamm G. W. The Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen 2 interacts with an EBNA2 responsive cis-element of the terminal protein 1 gene promoter. EMBO J. 1993 Jan;12(1):167–175. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05642.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimber-Strobl U., Suentzenich K. O., Laux G., Eick D., Cordier M., Calender A., Billaud M., Lenoir G. M., Bornkamm G. W. Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen 2 activates transcription of the terminal protein gene. J Virol. 1991 Jan;65(1):415–423. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.1.415-423.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]