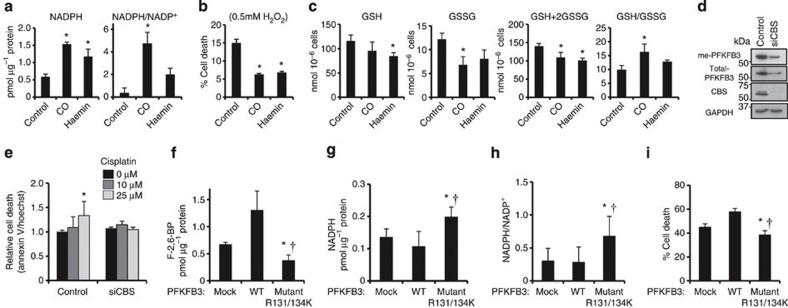
Figure 5. Protective effects of CO on oxidative cell injury through enhancing NADPH–glutathione system in U937 cells.
(a) Intracellular NADPH levels and NADPH/NADP+ ratio in U937 cells treated with CO or with haemin. Data indicate mean+s.d. (n=4–6). *P<0.05 versus controls. (b) Inhibitory effect of CO or haemin on H2O2-induced cell death. Cells were exposed to 0.5 mM H2O2 for 1 h. Data indicate mean+s.d. of four separate experiments *P<0.05 versus controls. (c) Alterations in reduced and oxidized glutathione levels in U937 cells treated with CO and haemin. Data indicate mean+s.d. (n=5–8). *P<0.05 versus controls. Procedures for treatment with CO at 5 μM for 30 min or with haemin at 25 μM for 6 h were identical throughout experiments. (d) The blot shows the methylation status of PFKFB3 in U937 cells transfected with siCBS. The expression level of GAPDH is used as a loading control. (e) Effect of CBS knockdown on cisplatin-induced apoptosis in U937 cells. U937 cells were treated with increasing concentrations of cisplatin for 6 hours. Cell viability was determined as fluorescence signal derived from annexin V-FITC in the apoptotic cells. Data indicate the values of relative cell death as means+s.d. of four separate experiments. *P<0.05 versus control without cisplatin treatment. Panels (f–i): Effects of overexpression of WT-PFKFB3 or mutant R131/134K-PFKFB3 on redox metabolites in HEK293 cells. (f) F-2,6-BP contents, (g) NADPH contents, (h) NADPH/NADP+ ratio and (i) sensitivity to H2O2. In these experiments, HEK293 cells were transfected with mock, WT or nonmethylable mutant (R131/134K) PFKFB3. Data indicate mean+s.d. of five separate experiments. *P<0.05 (mock versus R131/134K), †P<0.05 (WT versus R131/134K). ANOVA with Fischer’s multiple comparison test was used for determining statistical significance throughout this figure.