Abstract
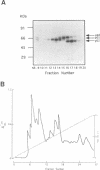
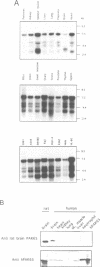
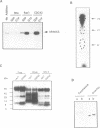
We identified three proteins in neutrophil cytosol of molecular size 65, 62 and 68 kDa which interact in a GTP-dependent manner with rac1 and CDC42Hs, but not with rho. Purification of p65 and subsequent peptide sequencing revealed identity to rat brain PAK65 and to yeast STE20 kinase domains. Based on these sequences we screened a human placenta library and cloned the full-length cDNA. The complete amino acid sequence of the human cDNA shares approximately identity with rat brain PAK65; within the kinase domain the human protein shares > 95% and approximately 63% identity with rat PAK65 and yeast STE20 respectively. The new human (h)PAK65 mRNA is ubiquitously expressed and hPAK65 protein is distinct from either human or rat brain PAK65. Recombinant hPAK65 exhibits identical specificity to the endogenous p65; both can bind rac1 and CDC42Hs in a GTP-dependent manner. The GTP-bound forms of rac1 and CDC42Hs induce autophosphorylation of hPAK65 on serine residues only. hPAK65 activated by either rac1 or CDC42Hs is phosphorylated on the same sites. Induction of hPAK65 autophosphorylation by rac1 or CDC42Hs stimulates hPAK65 kinase activity towards myelin basic protein and once hPAK65 is activated, rac1 or CDC42Hs are no longer required to keep it active. The affinities of rac/CDC42Hs for the non-phosphorylated and phosphorylated hPAK65 were similar. hPAK65 had only a marginal effect on the intrinsic GTPase activity of CDC42Hs, but significantly affected the binding and GAP activity of p190. These data are consistent with a model in which hPAK65 functions as an effector molecule for rac1 and CDC42Hs.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abo A., Pick E., Hall A., Totty N., Teahan C. G., Segal A. W. Activation of the NADPH oxidase involves the small GTP-binding protein p21rac1. Nature. 1991 Oct 17;353(6345):668–670. doi: 10.1038/353668a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Abo A., Webb M. R., Grogan A., Segal A. W. Activation of NADPH oxidase involves the dissociation of p21rac from its inhibitory GDP/GTP exchange protein (rhoGDI) followed by its translocation to the plasma membrane. Biochem J. 1994 Mar 15;298(Pt 3):585–591. doi: 10.1042/bj2980585. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Avruch J., Zhang X. F., Kyriakis J. M. Raf meets Ras: completing the framework of a signal transduction pathway. Trends Biochem Sci. 1994 Jul;19(7):279–283. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(94)90005-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boguski M. S., McCormick F. Proteins regulating Ras and its relatives. Nature. 1993 Dec 16;366(6456):643–654. doi: 10.1038/366643a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diekmann D., Abo A., Johnston C., Segal A. W., Hall A. Interaction of Rac with p67phox and regulation of phagocytic NADPH oxidase activity. Science. 1994 Jul 22;265(5171):531–533. doi: 10.1126/science.8036496. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Errede B., Gartner A., Zhou Z., Nasmyth K., Ammerer G. MAP kinase-related FUS3 from S. cerevisiae is activated by STE7 in vitro. Nature. 1993 Mar 18;362(6417):261–264. doi: 10.1038/362261a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Errede B., Levin D. E. A conserved kinase cascade for MAP kinase activation in yeast. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1993 Apr;5(2):254–260. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(93)90112-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grussenmeyer T., Scheidtmann K. H., Hutchinson M. A., Eckhart W., Walter G. Complexes of polyoma virus medium T antigen and cellular proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(23):7952–7954. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.23.7952. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gulbins E., Coggeshall K. M., Baier G., Katzav S., Burn P., Altman A. Tyrosine kinase-stimulated guanine nucleotide exchange activity of Vav in T cell activation. Science. 1993 May 7;260(5109):822–825. doi: 10.1126/science.8484124. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hart M. J., Eva A., Evans T., Aaronson S. A., Cerione R. A. Catalysis of guanine nucleotide exchange on the CDC42Hs protein by the dbl oncogene product. Nature. 1991 Nov 28;354(6351):311–314. doi: 10.1038/354311a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson D. I., Pringle J. R. Molecular characterization of CDC42, a Saccharomyces cerevisiae gene involved in the development of cell polarity. J Cell Biol. 1990 Jul;111(1):143–152. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.1.143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Juhl H., Soderling T. R. Peptide mapping and purification of phosphopeptides using high-performance liquid chromatography. Methods Enzymol. 1983;99:37–48. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)99038-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawasaki H., Suzuki K. Separation of peptides dissolved in a sodium dodecyl sulfate solution by reversed-phase liquid chromatography: removal of sodium dodecyl sulfate from peptides using an ion-exchange precolumn. Anal Biochem. 1990 May 1;186(2):264–268. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(90)90077-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khosravi-Far R., Chrzanowska-Wodnicka M., Solski P. A., Eva A., Burridge K., Der C. J. Dbl and Vav mediate transformation via mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways that are distinct from those activated by oncogenic Ras. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Oct;14(10):6848–6857. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.10.6848. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kishi K., Sasaki T., Kuroda S., Itoh T., Takai Y. Regulation of cytoplasmic division of Xenopus embryo by rho p21 and its inhibitory GDP/GTP exchange protein (rho GDI). J Cell Biol. 1993 Mar;120(5):1187–1195. doi: 10.1083/jcb.120.5.1187. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knaus U. G., Heyworth P. G., Evans T., Curnutte J. T., Bokoch G. M. Regulation of phagocyte oxygen radical production by the GTP-binding protein Rac 2. Science. 1991 Dec 6;254(5037):1512–1515. doi: 10.1126/science.1660188. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leberer E., Dignard D., Harcus D., Hougan L., Whiteway M., Thomas D. Y. Cloning of Saccharomyces cerevisiae STE5 as a suppressor of a Ste20 protein kinase mutant: structural and functional similarity of Ste5 to Far1. Mol Gen Genet. 1993 Nov;241(3-4):241–254. doi: 10.1007/BF00284675. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leberer E., Dignard D., Hougan L., Thomas D. Y., Whiteway M. Dominant-negative mutants of a yeast G-protein beta subunit identify two functional regions involved in pheromone signalling. EMBO J. 1992 Dec;11(13):4805–4813. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05586.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manser E., Leung T., Monfries C., Teo M., Hall C., Lim L. Diversity and versatility of GTPase activating proteins for the p21rho subfamily of ras G proteins detected by a novel overlay assay. J Biol Chem. 1992 Aug 15;267(23):16025–16028. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manser E., Leung T., Salihuddin H., Zhao Z. S., Lim L. A brain serine/threonine protein kinase activated by Cdc42 and Rac1. Nature. 1994 Jan 6;367(6458):40–46. doi: 10.1038/367040a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miki T., Smith C. L., Long J. E., Eva A., Fleming T. P. Oncogene ect2 is related to regulators of small GTP-binding proteins. Nature. 1993 Apr 1;362(6419):462–465. doi: 10.1038/362462a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nobes C., Hall A. Regulation and function of the Rho subfamily of small GTPases. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 1994 Feb;4(1):77–81. doi: 10.1016/0959-437x(94)90094-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramer S. W., Davis R. W. A dominant truncation allele identifies a gene, STE20, that encodes a putative protein kinase necessary for mating in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jan 15;90(2):452–456. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.2.452. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ridley A. J., Hall A. The small GTP-binding protein rho regulates the assembly of focal adhesions and actin stress fibers in response to growth factors. Cell. 1992 Aug 7;70(3):389–399. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90163-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ridley A. J., Paterson H. F., Johnston C. L., Diekmann D., Hall A. The small GTP-binding protein rac regulates growth factor-induced membrane ruffling. Cell. 1992 Aug 7;70(3):401–410. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90164-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segal A. W., Abo A. The biochemical basis of the NADPH oxidase of phagocytes. Trends Biochem Sci. 1993 Feb;18(2):43–47. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(93)90051-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Settleman J., Albright C. F., Foster L. C., Weinberg R. A. Association between GTPase activators for Rho and Ras families. Nature. 1992 Sep 10;359(6391):153–154. doi: 10.1038/359153a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shacter E. Organic extraction of Pi with isobutanol/toluene. Anal Biochem. 1984 May 1;138(2):416–420. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90831-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takaishi K., Kikuchi A., Kuroda S., Kotani K., Sasaki T., Takai Y. Involvement of rho p21 and its inhibitory GDP/GTP exchange protein (rho GDI) in cell motility. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Jan;13(1):72–79. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.1.72. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tominaga T., Sugie K., Hirata M., Morii N., Fukata J., Uchida A., Imura H., Narumiya S. Inhibition of PMA-induced, LFA-1-dependent lymphocyte aggregation by ADP ribosylation of the small molecular weight GTP binding protein, rho. J Cell Biol. 1993 Mar;120(6):1529–1537. doi: 10.1083/jcb.120.6.1529. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Totty N. F., Waterfield M. D., Hsuan J. J. Accelerated high-sensitivity microsequencing of proteins and peptides using a miniature reaction cartridge. Protein Sci. 1992 Sep;1(9):1215–1224. doi: 10.1002/pro.5560010914. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang J., King W. G., Dillon S., Hall A., Feig L., Rittenhouse S. E. Activation of platelet phosphatidylinositide 3-kinase requires the small GTP-binding protein Rho. J Biol Chem. 1993 Oct 25;268(30):22251–22254. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zheng Y., Bagrodia S., Cerione R. A. Activation of phosphoinositide 3-kinase activity by Cdc42Hs binding to p85. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jul 22;269(29):18727–18730. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]