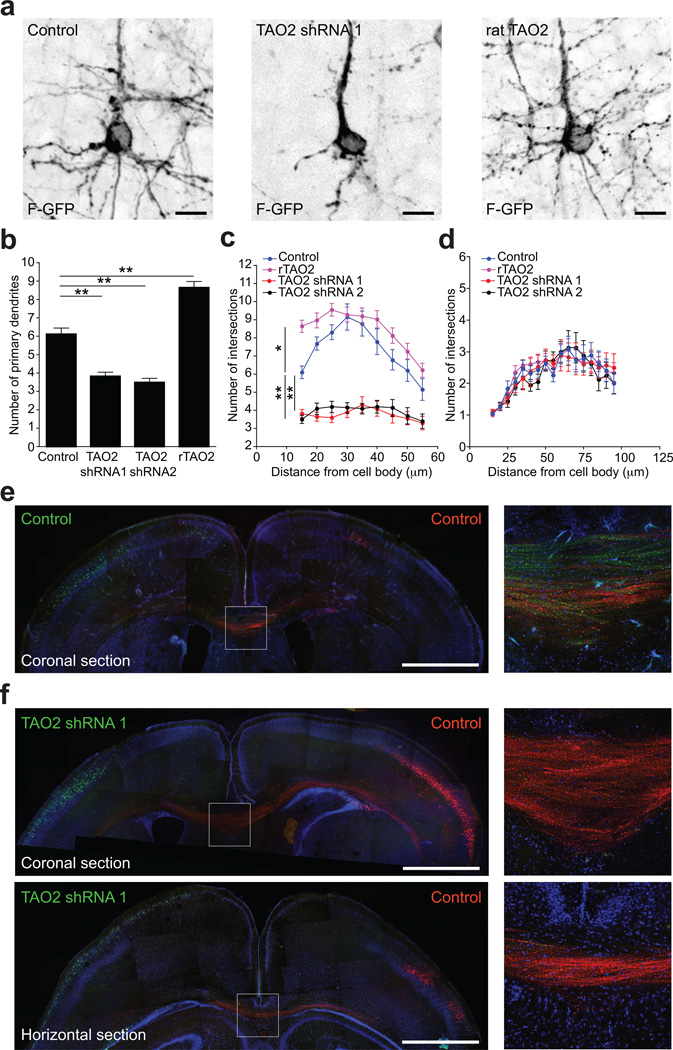
Figure 3. TAO2 down-regulation or over-expression affects basal dendrite arborization and callosal axon projection in the developing cortex.
(a) TAO2 knockdown or up-regulation have opposite effects in basal dendrite development in vivo. (b) The number of primary dendrites decreases following TAO2 knockdown and increases following rTAO2 over-expression (control: n=19 cells/three brains; TAO2 shRNA 1: n=23 cells/three brains; TAO2 shRNA 2: n=20 cells/two brains; rTAO2: n=31 cells/three brains; P<0.0001 by one-way ANOVA, posthoc Dunnett test **P <0.01). (c) Sholl analysis of the dendritic arbor from upper cortical layer transfected neurons (P<0.0001 by one-way ANOVA, posthoc Dunnett test **P <0.01, *P <0.05). (d) Sholl analysis of apical dendrites from cells in (c). (e, f) TAO2 shRNA-mediated down-regulation diminishes the number of callosal axons traversing the midline (n=3 brains per condition). (e) Control transfected neurons in both hemispheres (Venus: left hemisphere; mCherry: right hemisphere) project callosal axons that crossed the midline. Right panel: inset of the corpus callosum. (f) TAO2 knock-down in Venus-positive neurons prevents axons from these cells from crossing the midline. Upper panel: coronal brain section. Lower panel: horizontal brain section. Right panels: inset of the corpus callosum from the coronal (upper panel) and horizontal section (lower panel). Mean ± s.e.m. Scale bar: 10 µm (a) and 500 µm (e, f).