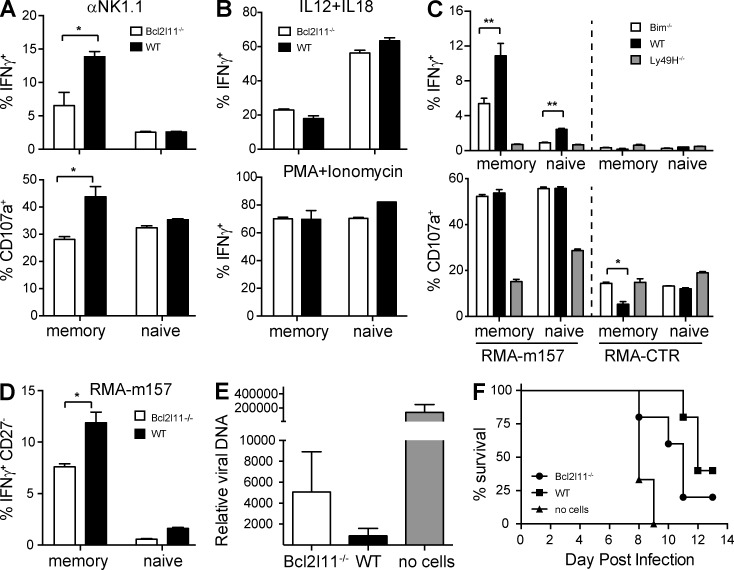
Figure 5.
Bim-deficient Ly49H+ memory NK cells are functionally impaired. Bcl2l11−/− and WT Ly49H+ memory NK cells generated by adoptive transfer were assessed at day 35 after MCMV. (A) Percentage of IFN-γ+ or CD107A+ Bcl2l11−/− or WT memory and naive NK cells after stimulation with plate-bound anti-NK1.1 is shown. (B) Percentage of IFN-γ+ Bcl2l11−/− or WT memory and naive NK cells after stimulation by IL12 + IL18 or PMA + ionomycin is shown. (C) Percentage of IFN-γ+ or CD107A+ Bcl2l11−/− or WT memory and naive NK cells after co-culture with m157-RMA or untransfected RMA cells is shown. Ly49H− NK cells are shown as a control. (D) The percentage of IFN-γ+CD27− Bcl2l11−/− or WT memory and naive NK cells is shown after stimulation by RMA-m157 cells. (E) 20,000 Bcl2l11−/− or WT Ly49H+ memory NK cells, or no Ly49H+ cells, were transferred into secondary Ly49H-deficient recipients and challenged with MCMV. Relative viral burden is shown in blood at day 3 p.i. (F) Survival of MCMV-infected Rag2−/− Ly49H-deficient mice receiving either Bcl2l11−/− or WT Ly49H+ memory NK cells, or no cells. Open bars represent Bcl2l11−/− Ly49H+ NK cells; black bars represent WT Ly49H+ NK cells (n = 4 mice for each condition). Data in each panel represent results from two to three independent experiments. Error bars signify the standard error of the mean. **, P < 0.01; *, P < 0.05.