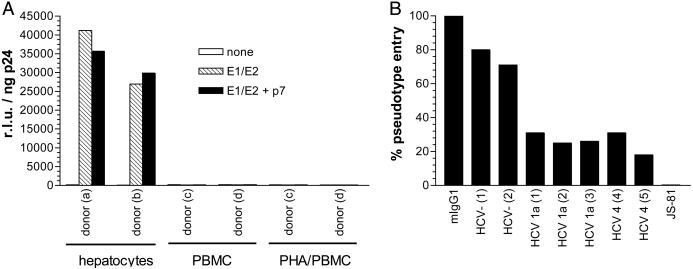
Fig. 1.
HCV pseudovirus entry into human primary cells. (A) Primary hepatocytes (≈104) from two healthy, HCV- donors were infected with NLluc+env- viruses (≈100 ng/ml p24) pseudotyped with no envelope glycoproteins, E1/E2, or E1/E2 coexpressed with p7. Similarly, PBMC (5 × 106) from healthy, HCV- donors were either infected or phytohemagglutinin-stimulated then infected with HCV pseudotypes. Luciferase activities (relative light units, r.l.u.) were measured 48 h postinfection and standardized for p24 content. Results are from a representative experiment. Entry into primary hepatocytes varied by ±100%. (B) Alternatively, primary hepatocytes were premixed with control murine IgG1 (10 μg/ml), sera (1:100) from two HCV-, two HCV subtype 1a+ and two HCV subtype 4+ donors, or anti-CD81 mAb JS-81 (10 μg/ml) immediately followed by infection with NLluc+env- viruses (≈100 ng/ml p24) pseudotyped with E1/E2. The % pseudovirus entry was calculated by (r.l.u. in the presence of inhibitor)/(r.l.u. in the absence of inhibitor) × 100%. Results are from a representative experiment with an assay error of ±25%.