Abstract
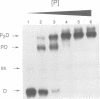
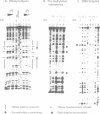
The dimeric AraC protein of Escherichia coli binds specifically to DNA sequences upstream of promoters whose transcription is regulated by arabinose. Here we show with affinity measurements, DNase footprinting, dimethyl sulfate premethylation interference and dimethyl sulfate footprinting studies that AraC protein can recognize paired half-sites in direct repeat orientation or inverted repeat orientation. A similar high degree of flexibility was also seen in the ability of the protein in the absence of arabinose to bind tightly and specifically when the separation of its half-sites was increased by 10 or 21 bp. In the presence of arabinose the protein could specifically contact both half-sites of a +10 bp spacing construct but could not contact both in a +21 bp construct. Reduced extensibility of AraC protein in the presence of arabinose provides a simple mechanism for the protein's shift from a non-inducing, DNA looping state to an inducing, non-looping state that contacts two adjacent half-sites at the arapBAD promoter.
Full text
PDF









Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brunelle A., Schleif R. Determining residue-base interactions between AraC protein and araI DNA. J Mol Biol. 1989 Oct 20;209(4):607–622. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90598-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bushuev V. N., Gudkov A. T., Liljas A., Sepetov N. F. The flexible region of protein L12 from bacterial ribosomes studied by proton nuclear magnetic resonance. J Biol Chem. 1989 Mar 15;264(8):4498–4505. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corton J. C., Johnston S. A. Altering DNA-binding specificity of GAL4 requires sequences adjacent to the zinc finger. Nature. 1989 Aug 31;340(6236):724–727. doi: 10.1038/340724a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curry J. F., Krause S. On the flexibility of myosin in solution. Biopolymers. 1991 Dec;31(14):1677–1687. doi: 10.1002/bip.360311403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drew H. R., Travers A. A. DNA structural variations in the E. coli tyrT promoter. Cell. 1984 Jun;37(2):491–502. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90379-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunn T. M., Hahn S., Ogden S., Schleif R. F. An operator at -280 base pairs that is required for repression of araBAD operon promoter: addition of DNA helical turns between the operator and promoter cyclically hinders repression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Aug;81(16):5017–5020. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.16.5017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunn T. M., Schleif R. Deletion analysis of the Escherichia coli ara PC and PBAD promoters. J Mol Biol. 1984 Nov 25;180(1):201–204. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90437-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ENGLESBERG E. Enzymatic characterization of 17 L-arabinose negative mutants of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1961 Jun;81:996–1006. doi: 10.1128/jb.81.6.996-1006.1961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Englesberg E., Irr J., Power J., Lee N. Positive control of enzyme synthesis by gene C in the L-arabinose system. J Bacteriol. 1965 Oct;90(4):946–957. doi: 10.1128/jb.90.4.946-957.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Englesberg E., Squires C., Meronk F., Jr The L-arabinose operon in Escherichia coli B-r: a genetic demonstration of two functional states of the product of a regulator gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Apr;62(4):1100–1107. doi: 10.1073/pnas.62.4.1100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galas D. J., Schmitz A. DNAse footprinting: a simple method for the detection of protein-DNA binding specificity. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 Sep;5(9):3157–3170. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.9.3157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenblatt J., Schleif R. Arabinose C protein: regulation of the arabinose operon in vitro. Nat New Biol. 1971 Oct 6;233(40):166–170. doi: 10.1038/newbio233166a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hahn S., Schleif R. In vivo regulation of the Escherichia coli araC promoter. J Bacteriol. 1983 Aug;155(2):593–600. doi: 10.1128/jb.155.2.593-600.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton E. P., Lee N. Three binding sites for AraC protein are required for autoregulation of araC in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Mar;85(6):1749–1753. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.6.1749. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrison S. C., Aggarwal A. K. DNA recognition by proteins with the helix-turn-helix motif. Annu Rev Biochem. 1990;59:933–969. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.59.070190.004441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hendrickson W., Schleif R. F. Regulation of the Escherichia coli L-arabinose operon studied by gel electrophoresis DNA binding assay. J Mol Biol. 1984 Sep 25;178(3):611–628. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90241-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hendrickson W., Schleif R. A dimer of AraC protein contacts three adjacent major groove regions of the araI DNA site. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(10):3129–3133. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.10.3129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hochschild A., Ptashne M. Cooperative binding of lambda repressors to sites separated by integral turns of the DNA helix. Cell. 1986 Mar 14;44(5):681–687. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90833-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huo L., Martin K. J., Schleif R. Alternative DNA loops regulate the arabinose operon in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Aug;85(15):5444–5448. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.15.5444. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jordan S. R., Pabo C. O. Structure of the lambda complex at 2.5 A resolution: details of the repressor-operator interactions. Science. 1988 Nov 11;242(4880):893–899. doi: 10.1126/science.3187530. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee D. H., Schleif R. F. In vivo DNA loops in araCBAD: size limits and helical repeat. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jan;86(2):476–480. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.2.476. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee N., Francklyn C., Hamilton E. P. Arabinose-induced binding of AraC protein to araI2 activates the araBAD operon promoter. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(24):8814–8818. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.24.8814. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lobell R. B., Schleif R. F. DNA looping and unlooping by AraC protein. Science. 1990 Oct 26;250(4980):528–532. doi: 10.1126/science.2237403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marmorstein R., Carey M., Ptashne M., Harrison S. C. DNA recognition by GAL4: structure of a protein-DNA complex. Nature. 1992 Apr 2;356(6368):408–414. doi: 10.1038/356408a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin K., Huo L., Schleif R. F. The DNA loop model for ara repression: AraC protein occupies the proposed loop sites in vivo and repression-negative mutations lie in these same sites. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(11):3654–3658. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.11.3654. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Menon K. P., Lee N. L. Activation of ara operons by a truncated AraC protein does not require inducer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 May;87(10):3708–3712. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.10.3708. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Menon K. P., Lee N. L. Activation of ara operons by a truncated AraC protein does not require inducer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 May;87(10):3708–3712. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.10.3708. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogden S., Haggerty D., Stoner C. M., Kolodrubetz D., Schleif R. The Escherichia coli L-arabinose operon: binding sites of the regulatory proteins and a mechanism of positive and negative regulation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jun;77(6):3346–3350. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.6.3346. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pabo C. O., Sauer R. T., Sturtevant J. M., Ptashne M. The lambda repressor contains two domains. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Apr;76(4):1608–1612. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.4.1608. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schleif R. DNA looping. Annu Rev Biochem. 1992;61:199–223. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.61.070192.001215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. L., Johnson A. D. A molecular mechanism for combinatorial control in yeast: MCM1 protein sets the spacing and orientation of the homeodomains of an alpha 2 dimer. Cell. 1992 Jan 10;68(1):133–142. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90212-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sosnick T. R., Benjamin D. C., Novotny J., Seeger P. A., Trewhella J. Distances between the antigen-binding sites of three murine antibody subclasses measured using neutron and X-ray scattering. Biochemistry. 1992 Feb 18;31(6):1779–1786. doi: 10.1021/bi00121a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steffen D., Schleif R. In vitro construction of plasmids which result in overproduction of the protein product of the araC gene of Escherichia coli. Mol Gen Genet. 1977 Dec 9;157(3):341–344. doi: 10.1007/BF00268672. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson C. C., Brown T. A., McKnight S. L. Convergence of Ets- and notch-related structural motifs in a heteromeric DNA binding complex. Science. 1991 Aug 16;253(5021):762–768. doi: 10.1126/science.1876833. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss M. A., Karplus M., Patel D. J., Sauer R. T. Solution NMR studies of intact lambda repressor. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 1983 Oct;1(1):151–157. doi: 10.1080/07391102.1983.10507431. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilcox G., Meuris P. Stabilization and size of araC protein. Mol Gen Genet. 1976 Apr 23;145(1):97–100. doi: 10.1007/BF00331563. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu H. M., Crothers D. M. The locus of sequence-directed and protein-induced DNA bending. Nature. 1984 Apr 5;308(5959):509–513. doi: 10.1038/308509a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]