Fig. 13.
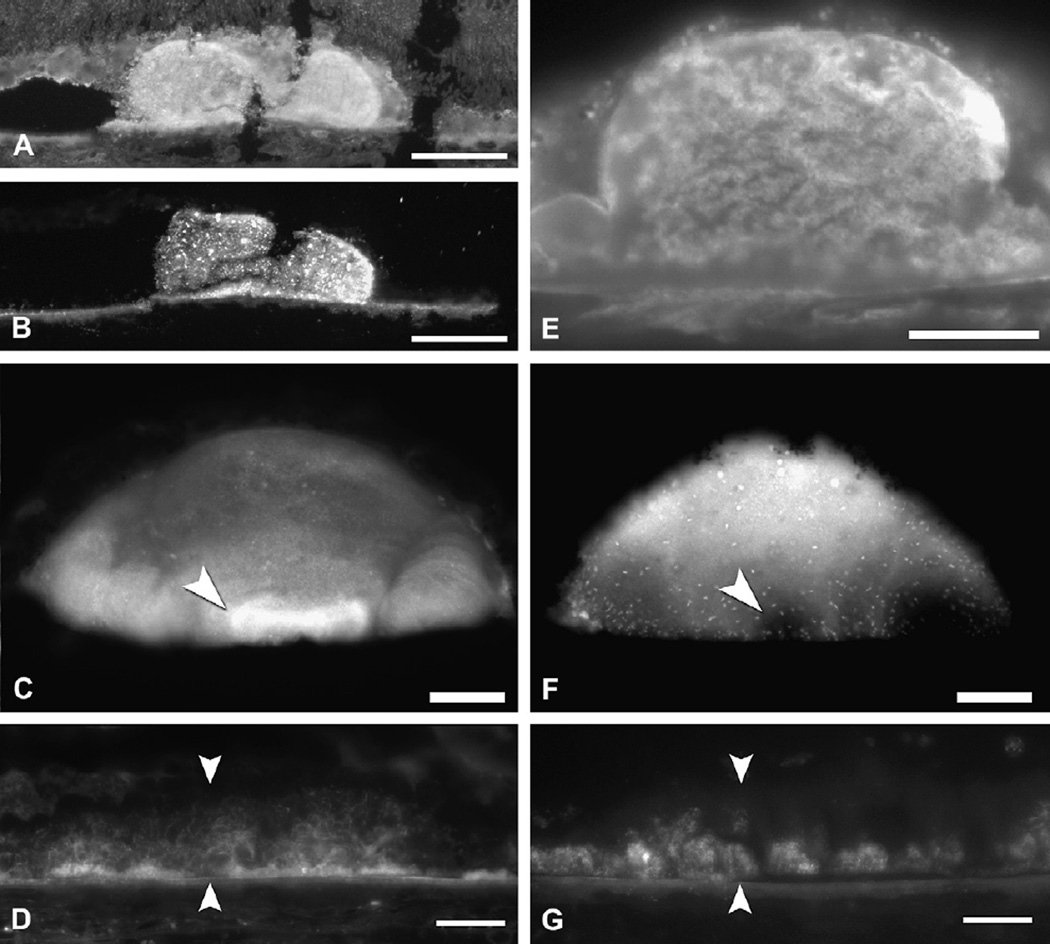
Cholesterol and apolipoproteins in drusen and deposits. Filipin fluorescence in A–D and F–G. Immunofluorescence in E. Bars in A, B, E 50 µm. Bars in C,D,F,G 20 µm. A. Druse and surrounding chorioretinal tissue contain UC. B. Druse (same as A) and BrM contain EC. Speckles represent lakes of EC. C. A bright UC-rich core (arrowhead) at the base of an isolated, extra-macular druse. D. A thick BlamD (between arrowheads) has bright, delicate fluorescence for UC. E. ApoB immunofluorescence in a druse. F. The core at the base of the same druse as panel C is EC-poor core (arrowhead). This druse also contains EC-rich lakes (speckles). G. A thick BlamD (same as D, between arrowheads) has fluorescence for EC confined to its outer half. Adapted from (Curcio et al., 2005a; Li et al., 2007; Malek et al., 2003).