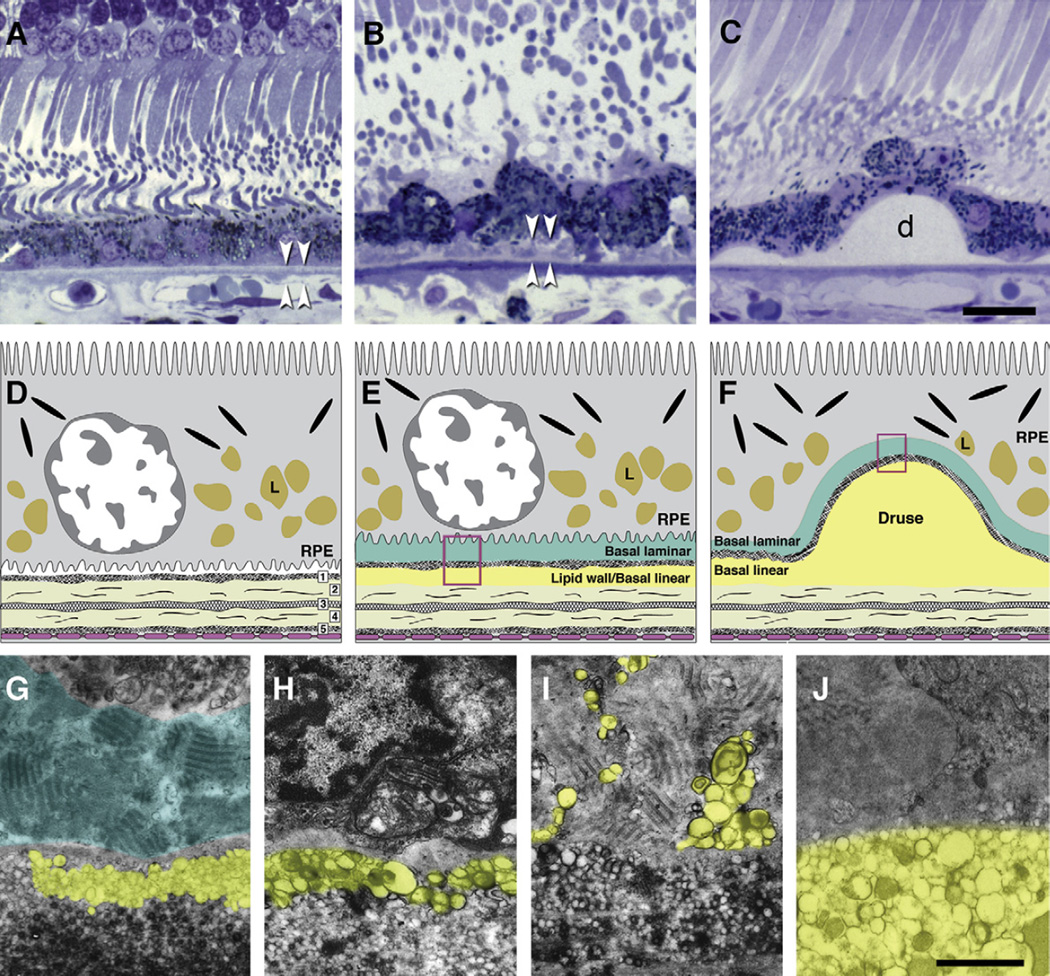
Fig. 2.
Bruch’s membrane and ARMD lesions. A–C: 1 µm sections, toluidine blue. Bar in C, 20 µm; A. Normal. RPE, BrM (arrowheads). B. Basal deposits (arrowheads) external to disrupted RPE. C: Druse (d). D–F: cartoons of extracellular lesions. D. BrM has 5 layers in a normal eye: 1, basal lamina of the RPE; 2, inner collagenous layer; 3, elastic layer; 4, outer collagenous layer; 5, basal lamina of the choriocapillary endothelium (fenestrated cells, pink). L, lipofuscin. E. An ARMD eye has basal laminar deposit (BlamD) and basal linear deposit (BlinD) and its precursor, the Lipid Wall. Boxed area is shown in panels G–I. F. Drusen, BlinD, and the Lipid Wall occupy the same plane. Boxed area is shown in panel J. G–J: colorized transmission electron micrographs. Aqua, basal laminar deposit (BlamD); yellow, BlinD, membranous debris, and Lipid Wall. Bar in J, 1 µm G. BlamD (aqua) and Lipid Wall (yellow). H. BlinD. I. Membranous debris crosses BlamD. J. Membranous debris within a large soft druse.