Abstract
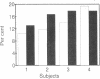
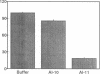
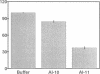
In human peripheral interstitial fluid, esterification of cholesterol by lecithin cholesterol acyltransferase (LCAT) was found to occur at a rate of only 10% of that in plasma (5.6 +/- 1.8 compared with 55.6 +/- 7.8 nmol/ml per h). Measurement of cholesterol esterification in the presence of excess reconstituted apoA-I HDL (rA-I HDL) revealed an LCAT activity in interstitial fluid of 24% of that in plasma, indicating that the low rate of esterification could not be caused by limiting mass of LCAT enzyme. When plasma was diluted to the same concentration as in interstitial fluid, the percent cholesterol esterification rate was the same as undiluted plasma and significantly higher than that of interstitial fluid. These findings led us to postulate that poor activation of LCAT in interstitial fluid may result from a change in conformation in apoA-I. To test this hypothesis, a monoclonal antibody AI-11 that inhibits apoA-I activation of LCAT was used to measure apoA-I in interstitial fluid and plasma. Antibody AI-11 recognized interstitial fluid apoA-I poorly, whereas a polyclonal antibody recognized interstitial fluid apoA-I normally. Incubation of antibody AI-11 with high density lipoprotein or rA-I HDL inhibited apoA-I activation of LCAT. We conclude that the altered conformation of apoA-I in interstitial fluid may render it a poor activator of LCAT.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anantharamaiah G. M., Venkatachalapathi Y. V., Brouillette C. G., Segrest J. P. Use of synthetic peptide analogues to localize lecithin:cholesterol acyltransferase activating domain in apolipoprotein A-I. Arteriosclerosis. 1990 Jan-Feb;10(1):95–105. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.10.1.95. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banka C. L., Bonnet D. J., Black A. S., Smith R. S., Curtiss L. K. Localization of an apolipoprotein A-I epitope critical for activation of lecithin-cholesterol acyltransferase. J Biol Chem. 1991 Dec 15;266(35):23886–23892. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonelli F. S., Jonas A. Reaction of lecithin cholesterol acyltransferase with water-soluble substrates. J Biol Chem. 1989 Sep 5;264(25):14723–14728. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castro G. R., Fielding C. J. Early incorporation of cell-derived cholesterol into pre-beta-migrating high-density lipoprotein. Biochemistry. 1988 Jan 12;27(1):25–29. doi: 10.1021/bi00401a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chung B. H., Anatharamaiah G. M., Brouillette C. G., Nishida T., Segrest J. P. Studies of synthetic peptide analogs of the amphipathic helix. Correlation of structure with function. J Biol Chem. 1985 Aug 25;260(18):10256–10262. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curtiss L. K., Edgington T. S. Immunochemical heterogeneity of human plasma high density lipoproteins. Identification with apolipoprotein A-I- and A-II-specific monoclonal antibodies. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 10;260(5):2982–2993. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curtiss L. K., Smith R. S. Localization of two epitopes of apolipoprotein A-I that are exposed on human high density lipoproteins using monoclonal antibodies and synthetic peptides. J Biol Chem. 1988 Sep 25;263(27):13779–13785. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dory L., Boquet L. M., Hamilton R. L., Sloop C. H., Roheim P. S. Heterogeneity of dog interstitial fluid (peripheral lymph) high density lipoproteins: implications for a role in reverse cholesterol transport. J Lipid Res. 1985 May;26(5):519–527. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dory L., Sloop C. H., Boquet L. M., Hamilton R. L., Roheim P. S. Lecithin:cholesterol acyltransferase-mediated modification of discoidal peripheral lymph high density lipoproteins: possible mechanism of formation of cholesterol-induced high density lipoproteins (HDLc) in cholesterol-fed dogs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(11):3489–3493. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.11.3489. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fielding P. E., Fielding C. J. A cholesteryl ester transfer complex in human plasma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jun;77(6):3327–3330. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.6.3327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaver A., Weedy N. K., Maldonado B. R., Huang S., Wong L. Procedure for development of an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Development of an assay for human apolipoprotein A-I. Clin Chim Acta. 1992 Jun 15;208(1-2):23–37. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(92)90020-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glomset J. A., Norum K. R. The metabolic role of lecithin: cholesterol acyltransferase: perspectives form pathology. Adv Lipid Res. 1973;11:1–65. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glomset J. A. The plasma lecithins:cholesterol acyltransferase reaction. J Lipid Res. 1968 Mar;9(2):155–167. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton R. L., Williams M. C., Fielding C. J., Havel R. J. Discoidal bilayer structure of nascent high density lipoproteins from perfused rat liver. J Clin Invest. 1976 Sep;58(3):667–680. doi: 10.1172/JCI108513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hogle D. M., Smith R. S., Curtiss L. K. Quantitation of plasma apolipoprotein A-I using two monoclonal antibodies in an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. J Lipid Res. 1988 Sep;29(9):1221–1229. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang J., Sloop C. H., Roheim P. S., Wong L. Lipoprotein lipase and hepatic triacylglycerol lipase activities in peripheral and skeletal muscle lymph. Arteriosclerosis. 1990 Sep-Oct;10(5):720–726. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.10.5.720. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jonas A., Sweeny S. A., Herbert P. N. Discoidal complexes of A and C apolipoproteins with lipids and their reactions with lecithin: cholesterol acyltransferase. J Biol Chem. 1984 May 25;259(10):6369–6375. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jonas A., Wald J. H., Toohill K. L., Krul E. S., Kézdy K. E. Apolipoprotein A-I structure and lipid properties in homogeneous, reconstituted spherical and discoidal high density lipoproteins. J Biol Chem. 1990 Dec 25;265(36):22123–22129. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joyner W. L., Carter R. D., Raizes G. S., Renkin E. M. Influence of histamine and some other substances on blood-lymph transport of plasma protein and dextran in the dog paw. Microvasc Res. 1974 Jan;7(1):19–30. doi: 10.1016/0026-2862(74)90034-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiistala U. Suction blister device for separation of viable epidermis from dermis. J Invest Dermatol. 1968 Feb;50(2):129–137. doi: 10.1038/jid.1968.15. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laurell C. B. Electroimmuno assay. Scand J Clin Lab Invest Suppl. 1972;124:21–37. doi: 10.3109/00365517209102748. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell C. D., King W. C., Applegate K. R., Forte T., Glomset J. A., Norum K. R., Gjone E. Characterization of apolipoprotein E-rich high density lipoproteins in familial lecithin:cholesterol acyltransferase deficiency. J Lipid Res. 1980 Jul;21(5):625–634. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pownall H. J., Hu A., Gotto A. M., Jr, Albers J. J., Sparrow J. T. Activation of lecithin:cholesterol acyltransferase by a synthetic model lipid-associating peptide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jun;77(6):3154–3158. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.6.3154. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reichl D., Miller N. E. Pathophysiology of reverse cholesterol transport. Insights from inherited disorders of lipoprotein metabolism. Arteriosclerosis. 1989 Nov-Dec;9(6):785–797. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.9.6.785. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reichl D., Simons L. A., Myant N. B., Pflug J. J., Mills G. L. The lipids and lipoproteins of human peripheral lymph, with observations on the transport of cholesterol from plasma and tissues into lymph. Clin Sci Mol Med. 1973 Sep;45(3):313–329. doi: 10.1042/cs0450313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodbard D., Lenox R. H., Wray H. L., Ramseth D. Statistical characterization of the random errors in the radioimmunoassay dose--response variable. Clin Chem. 1976 Mar;22(3):350–358. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sloop C. H., Dory L., Hamilton R., Krause B. R., Roheim P. S. Characterization of dog peripheral lymph lipoproteins: the presence of a disc-shaped "nascent" high density lipoprotein. J Lipid Res. 1983 Nov;24(11):1429–1440. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sloop C. H., Dory L., Krause B. R., Castle C., Roheim P. S. Lipoproteins and apolipoproteins in peripheral lymph of normal and cholesterol-fed dogs. Atherosclerosis. 1983 Oct;49(1):9–21. doi: 10.1016/0021-9150(83)90003-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sloop C. H., Dory L., Roheim P. S. Interstitial fluid lipoproteins. J Lipid Res. 1987 Mar;28(3):225–237. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stokke K. T., Fjeld N. B., Kluge T. H., Skrede S. Lipid composition and cholesterol esterification in lymph. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1974 May;33(3):199–206. doi: 10.3109/00365517409082488. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stokke K. T., Norum K. R. Determination of lecithin: cholesterol acyltransfer in human blood plasma. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1971 Feb;27(1):21–27. doi: 10.3109/00365517109080184. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vessby B., Gustafson S., Chapman M. J., Hellsing K., Lithell H. Lipoprotein composition of human suction-blister interstitial fluid. J Lipid Res. 1987 Jun;28(6):629–641. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]