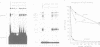Abstract
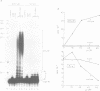
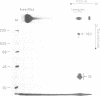
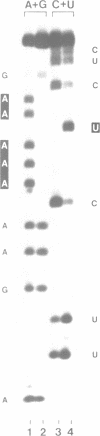
Cleavage and polyadenylation factor (CPF) is required for the cleavage as well as for the subsequent polyadenylation reaction during 3' processing of messenger RNA precursors. Here, we have investigated the interaction of CPF and poly(A) polymerase with short RNA substrates. CPF activates poly(A) polymerase to elongate RNA primers carrying the canonical hexamer recognition signal AAUAAA. CPF specifically binds to such RNA as shown by gel mobility shift assays and competition experiments. Upon binding of CPF, two polypeptides of 35 kDa and 160 kDa can be covalently crosslinked to the RNA by irradiation with UV light. These polypeptides may correspond to the smallest and the largest subunit contained in purified CPF fractions. In addition, chemical modification-exclusion experiments demonstrate that CPF interacts directly with the AAUAAA recognition signal in the RNA. The entire hexamer signal is involved in binding of CPF since modification of any of its bases interferes with complex formation.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bardwell V. J., Wickens M., Bienroth S., Keller W., Sproat B. S., Lamond A. I. Site-directed ribose methylation identifies 2'-OH groups in polyadenylation substrates critical for AAUAAA recognition and poly(A) addition. Cell. 1991 Apr 5;65(1):125–133. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90414-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bienroth S., Wahle E., Suter-Crazzolara C., Keller W. Purification of the cleavage and polyadenylation factor involved in the 3'-processing of messenger RNA precursors. J Biol Chem. 1991 Oct 15;266(29):19768–19776. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnstiel M. L., Busslinger M., Strub K. Transcription termination and 3' processing: the end is in site! Cell. 1985 Jun;41(2):349–359. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80007-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calnan B. J., Tidor B., Biancalana S., Hudson D., Frankel A. D. Arginine-mediated RNA recognition: the arginine fork. Science. 1991 May 24;252(5009):1167–1171. doi: 10.1126/science.252.5009.1167. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christofori G., Keller W. 3' cleavage and polyadenylation of mRNA precursors in vitro requires a poly(A) polymerase, a cleavage factor, and a snRNP. Cell. 1988 Sep 9;54(6):875–889. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(88)91263-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christofori G., Keller W. Poly(A) polymerase purified from HeLa cell nuclear extract is required for both cleavage and polyadenylation of pre-mRNA in vitro. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Jan;9(1):193–203. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.1.193. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conway L., Wickens M. Analysis of mRNA 3' end formation by modification interference: the only modifications which prevent processing lie in AAUAAA and the poly(A) site. EMBO J. 1987 Dec 20;6(13):4177–4184. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02764.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Draper D. E. How do proteins recognize specific RNA sites? New clues from autogenously regulated ribosomal proteins. Trends Biochem Sci. 1989 Aug;14(8):335–338. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(89)90167-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dreyfuss G. Structure and function of nuclear and cytoplasmic ribonucleoprotein particles. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1986;2:459–498. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.02.110186.002331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frendewey D., Krämer A., Keller W. Different small nuclear ribonucleoprotein particles are involved in different steps of splicing complex formation. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1987;52:287–298. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1987.052.01.034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilmartin G. M., McDevitt M. A., Nevins J. R. Multiple factors are required for specific RNA cleavage at a poly(A) addition site. Genes Dev. 1988 May;2(5):578–587. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.5.578. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilmartin G. M., Nevins J. R. An ordered pathway of assembly of components required for polyadenylation site recognition and processing. Genes Dev. 1989 Dec;3(12B):2180–2190. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.12b.2180. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilmartin G. M., Nevins J. R. Molecular analyses of two poly(A) site-processing factors that determine the recognition and efficiency of cleavage of the pre-mRNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 May;11(5):2432–2438. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.5.2432. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Humphrey T., Christofori G., Lucijanic V., Keller W. Cleavage and polyadenylation of messenger RNA precursors in vitro occurs within large and specific 3' processing complexes. EMBO J. 1987 Dec 20;6(13):4159–4168. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02762.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson R. J., Standart N. Do the poly(A) tail and 3' untranslated region control mRNA translation? Cell. 1990 Jul 13;62(1):15–24. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90235-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lang K. M., Keller W. Sequence requirements in different steps of the pre-mRNA splicing reaction: analysis by the RNA modification-exclusion technique. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Sep;10(9):4942–4947. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.9.4942. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDevitt M. A., Gilmartin G. M., Reeves W. H., Nevins J. R. Multiple factors are required for poly(A) addition to a mRNA 3' end. Genes Dev. 1988 May;2(5):588–597. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.5.588. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore C. L., Chen J., Whoriskey J. Two proteins crosslinked to RNA containing the adenovirus L3 poly(A) site require the AAUAAA sequence for binding. EMBO J. 1988 Oct;7(10):3159–3169. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03183.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore C. L., Sharp P. A. Accurate cleavage and polyadenylation of exogenous RNA substrate. Cell. 1985 Jul;41(3):845–855. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80065-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peattie D. A. Direct chemical method for sequencing RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Apr;76(4):1760–1764. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.4.1760. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Proudfoot N. Poly(A) signals. Cell. 1991 Feb 22;64(4):671–674. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90495-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rymond B. C., Rosbash M. A chemical modification/interference study of yeast pre-mRNA spliceosome assembly and splicing. Genes Dev. 1988 Apr;2(4):428–439. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.4.428. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steitz T. A. Structural studies of protein-nucleic acid interaction: the sources of sequence-specific binding. Q Rev Biophys. 1990 Aug;23(3):205–280. doi: 10.1017/s0033583500005552. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takagaki Y., Manley J. L., MacDonald C. C., Wilusz J., Shenk T. A multisubunit factor, CstF, is required for polyadenylation of mammalian pre-mRNAs. Genes Dev. 1990 Dec;4(12A):2112–2120. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.12a.2112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takagaki Y., Ryner L. C., Manley J. L. Four factors are required for 3'-end cleavage of pre-mRNAs. Genes Dev. 1989 Nov;3(11):1711–1724. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.11.1711. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takagaki Y., Ryner L. C., Manley J. L. Separation and characterization of a poly(A) polymerase and a cleavage/specificity factor required for pre-mRNA polyadenylation. Cell. 1988 Mar 11;52(5):731–742. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90411-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahle E. A novel poly(A)-binding protein acts as a specificity factor in the second phase of messenger RNA polyadenylation. Cell. 1991 Aug 23;66(4):759–768. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90119-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahle E. Purification and characterization of a mammalian polyadenylate polymerase involved in the 3' end processing of messenger RNA precursors. J Biol Chem. 1991 Feb 15;266(5):3131–3139. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss E. A., Gilmartin G. M., Nevins J. R. Poly(A) site efficiency reflects the stability of complex formation involving the downstream element. EMBO J. 1991 Jan;10(1):215–219. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07938.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wickens M. How the messenger got its tail: addition of poly(A) in the nucleus. Trends Biochem Sci. 1990 Jul;15(7):277–281. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(90)90054-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wigley P. L., Sheets M. D., Zarkower D. A., Whitmer M. E., Wickens M. Polyadenylation of mRNA: minimal substrates and a requirement for the 2' hydroxyl of the U in AAUAAA. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Apr;10(4):1705–1713. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.4.1705. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilusz J., Pettine S. M., Shenk T. Functional analysis of point mutations in the AAUAAA motif of the SV40 late polyadenylation signal. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 May 25;17(10):3899–3908. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.10.3899. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witherell G. W., Gott J. M., Uhlenbeck O. C. Specific interaction between RNA phage coat proteins and RNA. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1991;40:185–220. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60842-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zarkower D., Stephenson P., Sheets M., Wickens M. The AAUAAA sequence is required both for cleavage and for polyadenylation of simian virus 40 pre-mRNA in vitro. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jul;6(7):2317–2323. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.7.2317. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]