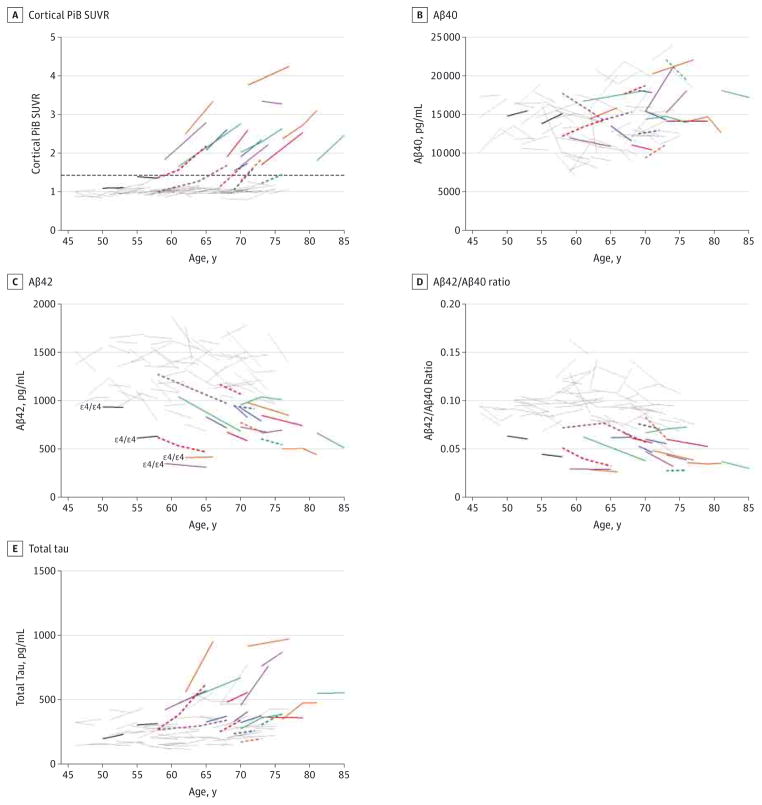
Figure 3. Association Between Longitudinal Patterns of Cerebrospinal Fluid Biomarkers Cortical Pittsburgh Compound B (PiB) Standardized Uptake Value Ratio (SUVR), β-Amyloid 40 (Aβ40), Aβ42, Aβ42 to Aβ40 Ratio, and Total Tau, Cortical Amyloid, and Age.
A subset (n = 74) of Adult Children Study participants had undergone longitudinal amyloid imaging via PiB positron emission tomographic imaging within 376 days (mean [SD], 84.3 [92] days) of cerebrospinal fluid collection. Biomarker measures include cortical PiB SUVR (A), Aβ40 (B), Aβ42 (C), Aβ42 to Aβ40 ratio (D), and total tau (E). The Aβ40, Aβ42, and total tau were analyzed by INNOTEST enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (Fujirebio Europe). Being PiB positive was defined as having a mean cortical PiB SUVR higher than 1.42 and is represented by the dashed horizontal line in panel A. Gray lines indicate PiB negative at baseline and follow-up (n = 52); solid colored lines, PiB positive at both baseline and follow-up (n = 14); dashed colored lines, PiB negative at baseline but positive at follow-up (n = 6); and solid black lines, PiB negative with discordant (low) cerebrospinal fluid Aβ measures at baseline and follow-up (n = 2). Colored solid and dashed lines are each differently colored only to facilitate visual comparisons across all analytes for each PiB-positive individual.