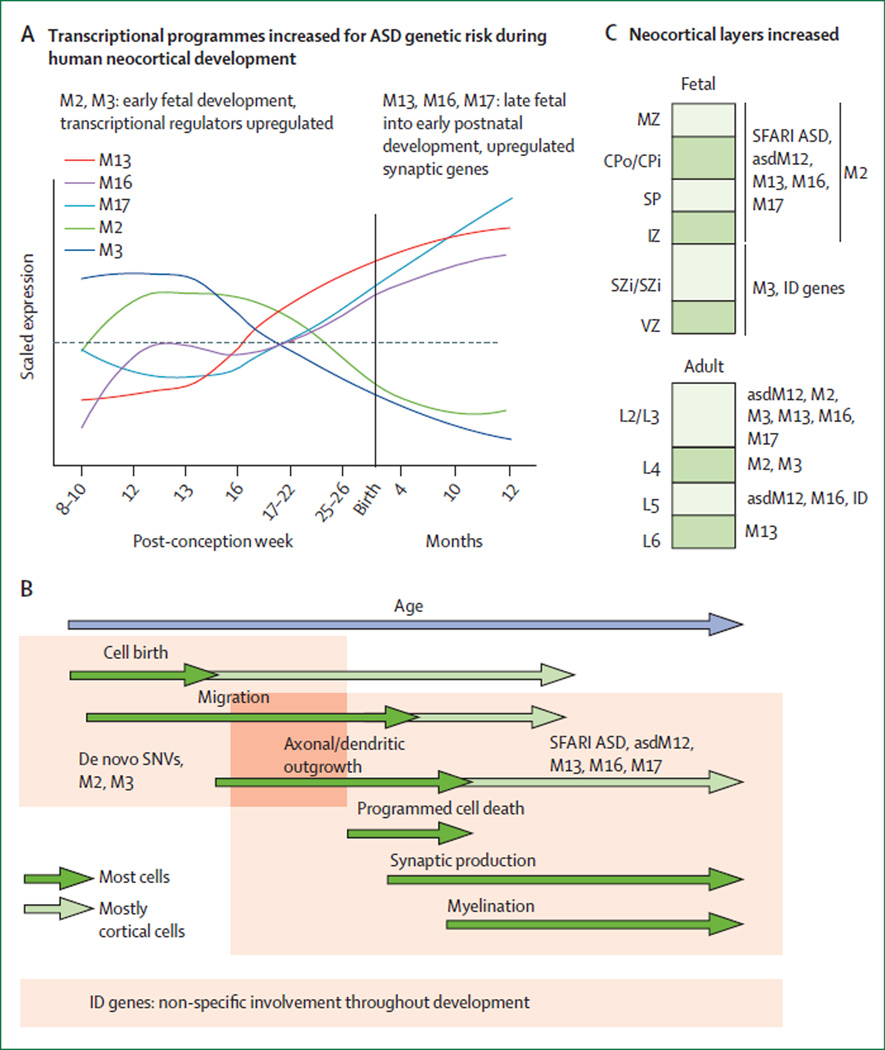
Figure 1. A model of the effects of gene sets implicated in autism spectrum disorder.
(A) Autism spectrum disorder (ASD) risk genes from several sources, including mutations identified by exome sequencing60,61,63,65 of candidate genes from the Simons Foundation Autism Research Initiative (SFARI) database and neuronal genes dysregulated in the post-mortem brains of people with ASD,66 were compiled as described in detail by Parikshak and colleagues.67 ASD risk genes were differentially enriched in five co-expression modules throughout development: M2, M3, M13, M16, and M17. (B) Early transcriptional regulators in M2/M3 are enriched for rare de novo variants (RDNVs), whereas the later-expressed synaptic genes in M13, M16, and M17 are associated with previously studied ASD candidate genes compiled in the SFARI database and dysregulated in the post-mortem brain tissue from patients diagnosed with an ASD. By contrast with ASD genes, more than 400 known mendelian intellectual disability (ID) risk genes compiled from multiple sources68 were not enriched for specific developmental trajectories. (C) By using publicly available gene expression data from specific cell types or cortical laminae, ASD risk genes were found to be more consistently associated with post-mitotic laminae during early fetal development (IZ, SP, CPo/CPi, and MZ) and upper cortical layers in adults (L2 or L3, and RDNV-associated genes in L4). Several gene co-expression modules that correspond to specific processes in brain development that are enriched for ASD genes are also strongly associated with markers of upper-layer glutamatergic neurons in adult cortex, which suggests that many ASD genes preferentially affect these cell types. Work from Willsey and colleagues59 identified a subset of genes enriched in lower-layer neurons, but overall supported enrichment in glutamatergic neurons. SNV=single-nucleotide variant. MZ=marginal zone. CPo=outer cortical plate. CPi=inner cortical plate. SP=subplate zone. IZ=intermediate zone. SZi=inner subventricular zone. VZ=ventricular zone. Adapted with permission from Parikshak and colleagues.67