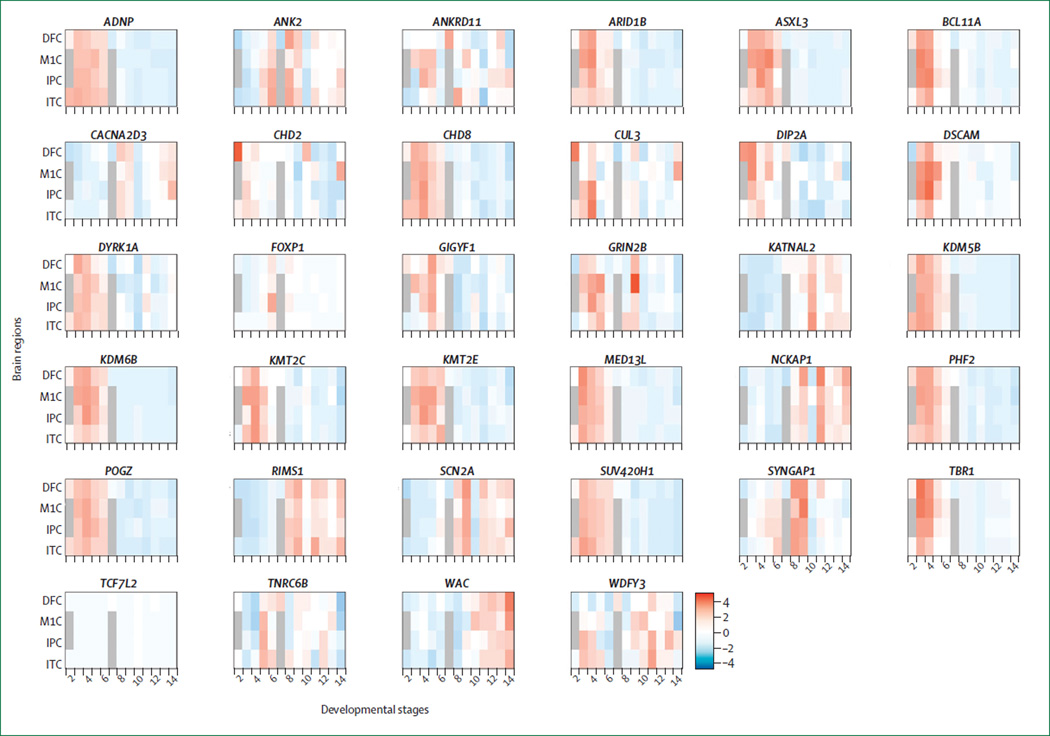
Figure 2. Developmental and regional expression patterns of newly identified recurrently mutated risk genes in autism spectrum disorder.
Heat map depicting gene expression patterns in various brain regions throughout development for each of the recurrently mutated autism spectrum disorder (ASD) risk genes depicted in the table, using gene expression data adapted from Kang and colleagues.86 The colour code is scaled from red (high expression) to blue (low expression). Developmental stages range from post-conception week 4–8 (stage 1) and mid-gestation (stages 4–6), through birth to 6 months (stage 8), and into adulthood (stage 13 and beyond). Most genes have very circumscribed developmental gradients of expression, showing either high fetal expression (eg, chromatin and transcriptional regulatory genes) or a postnatal increase concomitant with neuronal maturation (eg, synaptic signalling genes). DFC=dorsolateral prefrontal cortex. M1C=primary motor (M1) cortex. IPC=inferior parietal cortex. ITC=inferior temporal cortex.