Abstract
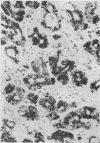
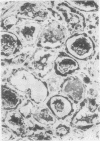
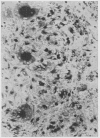
The distribution of muramidase (lysozyme) in normal and pathological human tissues has been studied, using an immunohistological technique. The enzyme was demonstrated in a variety of healthy tissues, including serous salivary acinar cells, lactating mammary tissue, Paneth cells, renal tubular cells, myeloid cells (including eosinophils), and histiocytic cells. In pathological tissues the most striking positivity was encountered in reactive histiocytic cells in granulomatous conditions such as tuberculosis and Crohn's disease. The finding of this study are related to previous reports of the distribution of human and animal muramidase and the implications of patterns of muramidase staining in pathological histiocytes are briefly discussed.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andersen E., Videbaek A. Stem cell leukaemia in myelomatosis. Scand J Haematol. 1970;7(3):201–207. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0609.1970.tb01888.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Asamer H., Schmalzl F., Braunsteiner H. Immunocytological demonstration of lysozyme (muramidase) in human leukaemic cells. Br J Haematol. 1971 Jun;20(6):571–574. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1971.tb00795.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balazs T., Roepke R. R. Lysozymuria induced in rats by nephrotoxic agents. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1966 Nov;123(2):380–385. doi: 10.3181/00379727-123-31494. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Briggs R. S., Perillie P. E., Finch S. C. Lysozyme in bone marrow and peripheral blood cells. J Histochem Cytochem. 1966 Feb;14(2):167–170. doi: 10.1177/14.2.167. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burns J., Hambridge M., Taylor C. R. Intracellular immunoglobulins. A comparative study on three standard tissue processing methods using horseradish peroxidase and fluorochrome conjugates. J Clin Pathol. 1974 Jul;27(7):548–557. doi: 10.1136/jcp.27.7.548. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CAPPUCCINO J. G., WINSTON S., PERRI G. C. MURAMIDASE ACTIVITY OF KIDNEY AND SPLEEN IN SWISS MICE CHALLENGED WITH B.C.G., ZYMOSAN AND BACTERIAL ENDOTOXINS. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1964 Aug-Sep;116:869–872. doi: 10.3181/00379727-116-29393. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catovsky D., Galton D. A., Griffin C. The significance of lysozyme estimations in acute myeloid and chronic monocytic leukaemia. Br J Haematol. 1971 Nov;21(5):565–580. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1971.tb02718.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenstein R., Arsenis C., Kuettner K. E. Electron microscopic studies of cartilage matrix using lysozyme as a vital stain. J Cell Biol. 1970 Sep;46(3):626–631. doi: 10.1083/jcb.46.3.626. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erlandsen S. L., Chase D. G. Paneth cell function: phagocytosis and intracellular digestion of intestinal microorganisms. I. Hexamita muris. J Ultrastruct Res. 1972 Nov;41(3):296–318. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(72)90071-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FINCH S. C., LAMPHERE J. P., JABLON S. THE RELATIONSHIP OF SERUM LYSOZYME TO LEUKOCYTES AND OTHER CONSTITUTIONAL FACTORS. Yale J Biol Med. 1964 Apr;36:350–360. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fink M. E., Finch S. C. Serum muramidase and granulocyte turnover. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1968 Feb;127(2):365–367. doi: 10.3181/00379727-127-32692. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GLYNN A. A., PARKMAN R. STUDIES WITH AN ANTIBODY TO RAT LYSOZYME. Immunology. 1964 Nov;7:724–729. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghoos Y., Vantrappen G. The cytochemical localization of lysozyme activity in leucocytes. Histochem J. 1970 Jan;2(1):11–16. doi: 10.1007/BF01003451. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghoos Y., Vantrappen G. The cytochemical localization of lysozyme in Paneth cell granules. Histochem J. 1971 May;3(3):175–178. doi: 10.1007/BF01002560. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glynn A. A. Lysozyme: antigen, enzyme and antibacterial agent. Sci Basis Med Annu Rev. 1968:31–52. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenwald R. A., Josephson A. S., Diamond H. S., Tsang A. Human cartilage lysozyme. J Clin Invest. 1972 Sep;51(9):2264–2270. doi: 10.1172/JCI107035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenwald R. A., Sajdera S. W. Extracellular localization of lysozyme in rachitic rat cartilage. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1973 Mar;142(3):924–927. doi: 10.3181/00379727-142-37145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klockars M., Osserman E. F. Localization of lysozyme in normal rat tissues by an immunoperoxidase method. J Histochem Cytochem. 1974 Mar;22(3):139–146. doi: 10.1177/22.3.139. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osserman E. F., Lawlor D. P. Serum and urinary lysozyme (muramidase) in monocytic and monomyelocytic leukemia. J Exp Med. 1966 Nov 1;124(5):921–952. doi: 10.1084/jem.124.5.921. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SPEECE A. J. HISTOCHEMICAL DISTRIBUTION OF LYSOZYME ACTIVITY IN ORGANS OF NORMAL MICE AND RADIATION CHIMERAS. J Histochem Cytochem. 1964 May;12:384–391. doi: 10.1177/12.5.384. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scholnik A. P., Kass L. A direct cytochemical method for the identification of lysozyme in various tissues. J Histochem Cytochem. 1973 Jan;21(1):65–72. doi: 10.1177/21.1.65. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sternberger L. A., Hardy P. H., Jr, Cuculis J. J., Meyer H. G. The unlabeled antibody enzyme method of immunohistochemistry: preparation and properties of soluble antigen-antibody complex (horseradish peroxidase-antihorseradish peroxidase) and its use in identification of spirochetes. J Histochem Cytochem. 1970 May;18(5):315–333. doi: 10.1177/18.5.315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sternberger L. A., Osserman E. F., Seligman A. M. Lysozyme and fibrinogen in normal and leukemic blood cells: a quantitative electron immunocytochemical study. Johns Hopkins Med J. 1970 Apr;126(4):188–209. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Syrén E., Raeste A. M. Identification of blood monocytes by demonstration of lysozyme and peroxidase activity. Acta Haematol. 1971;45(1):29–35. doi: 10.1159/000208604. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor C. R., Burns J. The demonstration of plasma cells and other immunoglobulin-containing cells in formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded tissues using peroxidase-labelled antibody. J Clin Pathol. 1974 Jan;27(1):14–20. doi: 10.1136/jcp.27.1.14. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor C. R., Mason D. Y. The immunohistological detection of intracellular immunoglobulin in formalin-paraffin sections from multiple myeloma and related conditions using the immunoperoxidase technique. Clin Exp Immunol. 1974 Nov;18(3):417–429. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor C. R. The nature of Reed-Sternberg cells and other malignant "reticulum" cells. Lancet. 1974 Oct 5;2(7884):802–807. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(74)91071-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]