Figure 4.
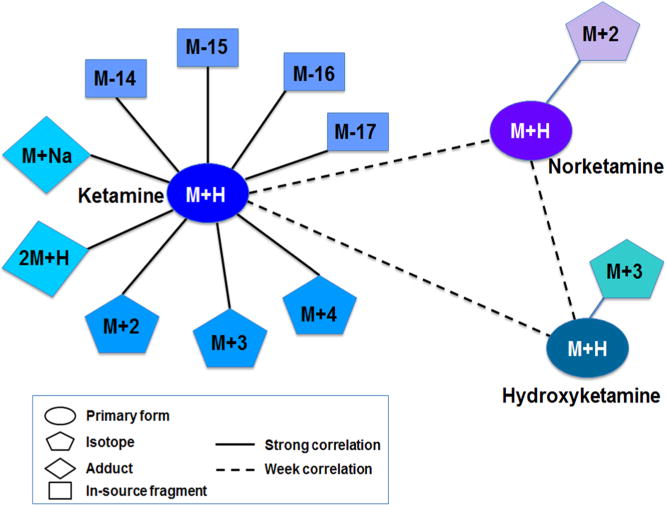
Correlation-based network analysis to identify related ions and metabolites. Data-driven network analysis can be used to identify modules/clusters of strongly associated ions. Some of these associations are a consequence of analytical correlations, such as multiple adducts formed from a single chemical, while other associations are a consequence of biological relationships. In the example shown here for the anesthetic ketamine, each subcluster shows strong associations between the primary form, adducts, isotopes, and ionization fragments derived from the same metabolite. Secondary correlations exist between biologically related metabolites, ketamine and its metabolites, norketamine, and hydroxyketamine. Data are from the studies of Jones et al. and Uppal et al.19,64
