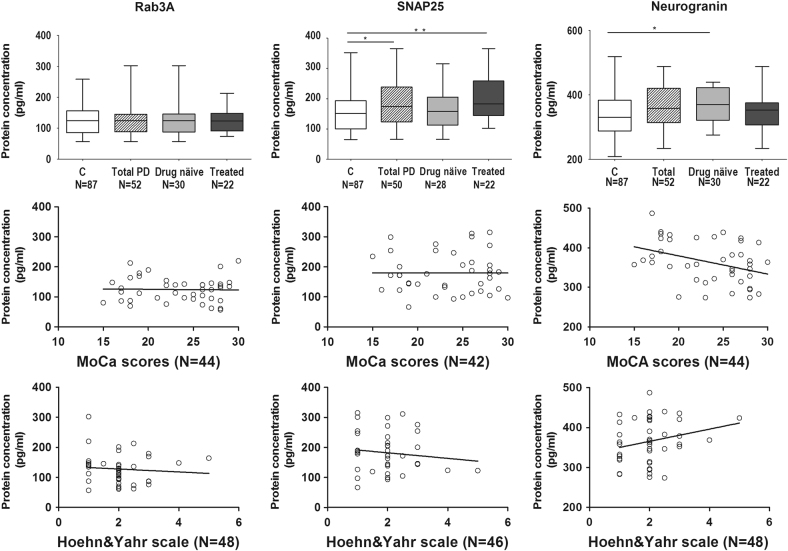
Fig. 1.
Changes in the CSF concentration of synaptic proteins neurogranin, Rab3A and SNAP25 and their clinical correlates. Concentration of synaptosome associated protein SNAP25 (b) measured by ELISA present overall increase in the PD patient group while presynaptic vesicle protein Rab3A (a) and postsynaptic protein neurogranin (c) concentrations remained unchanged in CSF of patients diagnosed with Parkinson disease compared to control participants. In the subgroup of drug naïve patients concentrations of neurogranin were elevated compared to control patients. Statistical analyses were performed using Mann-Whitney U test. p-value < 0.05 was considered significant. Neurogranin protein concentration presents significant negative correlation with cognitive impairment of PD patients assessed by MoCA scores. There were no significant correlations observed between Rab3A or SNAP25 and cognitive assessment. Neurogranin presented significant correlation with disease stage. There were no significant associations between disease stage and presynaptic proteins. The bars represent the mean values with inter-quartile range. Abbreviations used “C control”, “PD Parkinson’s disease”