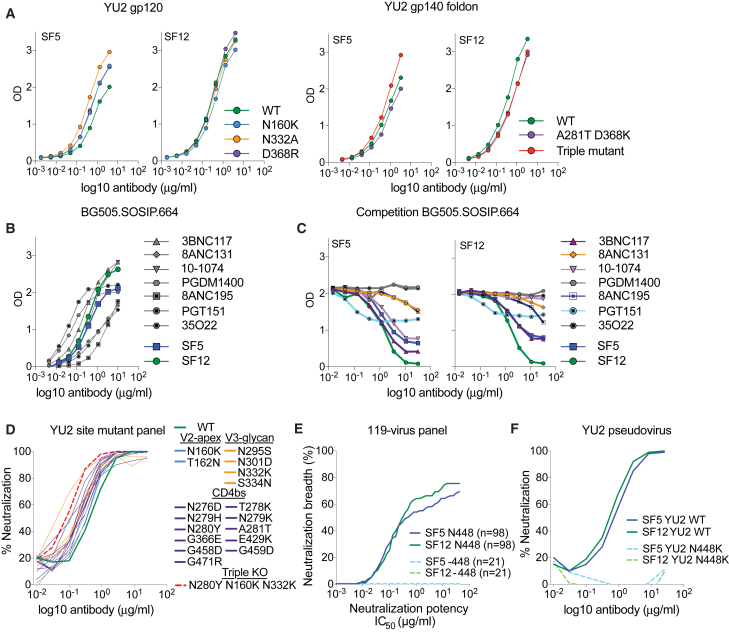
Figure 2.
Antibodies SF5 and SF12 Bind a Distinct Epitope on the gp120 Portion of Env
(A) ELISA of SF5 and SF12 against a gp120 monomer and a gp140 foldon trimer derived from HIV-1 strain YU2. Wild-type proteins and various site mutants of the proteins in common bNAb epitopes (CD4-binding site, V3-glycan, Apex) were tested. Triple mutant = N160K, A281T + D368K, N332K. Data representative of 3 repeat assays.
(B) ELISA of SF5 and SF12 as well as reference bNAbs targeting 6 known epitopes against the BG505.SOSIP.664 trimer. Data representative of 3 repeat assays.
(C) Competition ELISA with reference bNAbs targeting 6 known epitopes to evaluate interference with SF5 and SF12 binding to the BG505.SOSIP.664 trimer. Competing antibodies were added in a dilution series starting at 32 μg/mL. SF5 and SF12 were added at a constant concentration of 0.5 μg/mL. Data representative of 3 repeat assays.
(D) Neutralization testing of SF12 against a panel of YU2 site mutants covering major epitopes on the HIV-1 spike. Neutralization testing performed in duplicates, average curves shown.
(E) Computational analysis of 119-virus cross clade panel neutralization.
(F) Neutralization testing of SF5 and SF12 against an HIV-1 pseudovirus based on strain YU2 carrying a mutation at the PNGS N448gp120. Testing done in duplicates, average shown.