Abstract
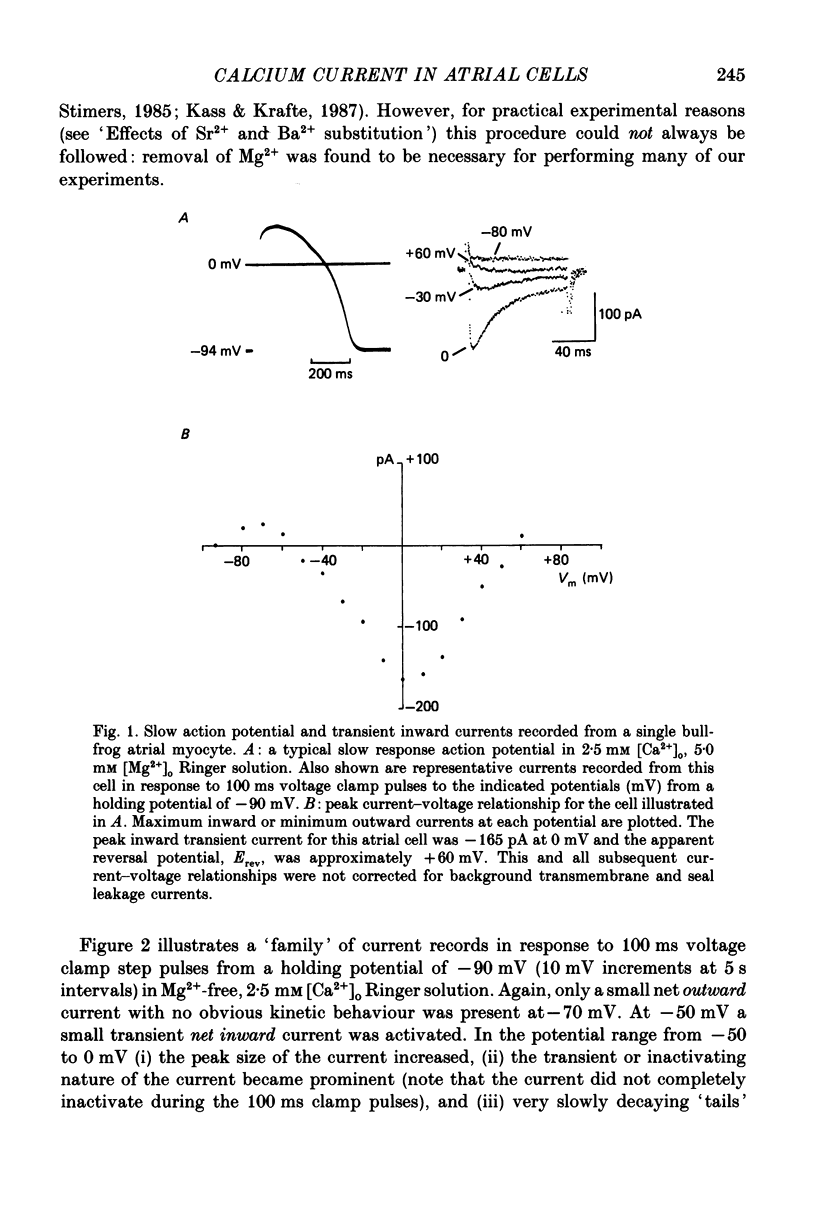
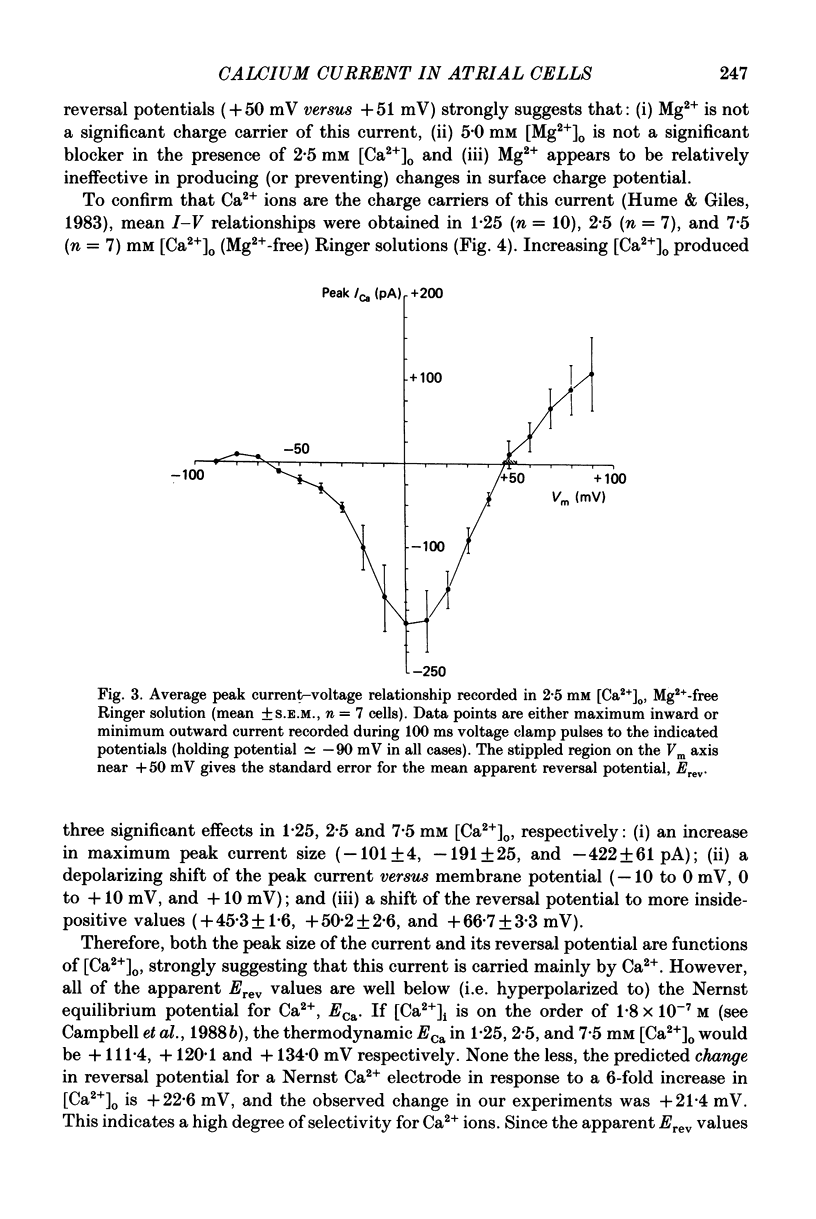
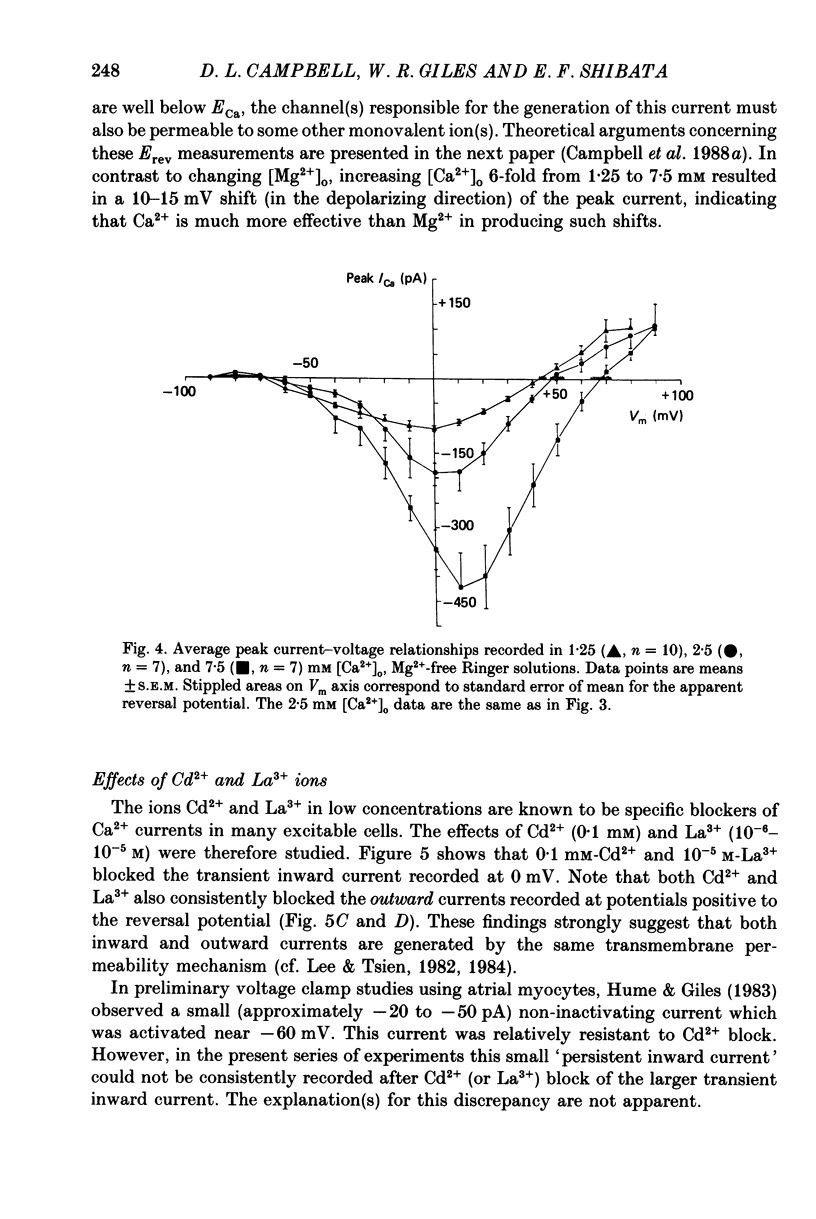
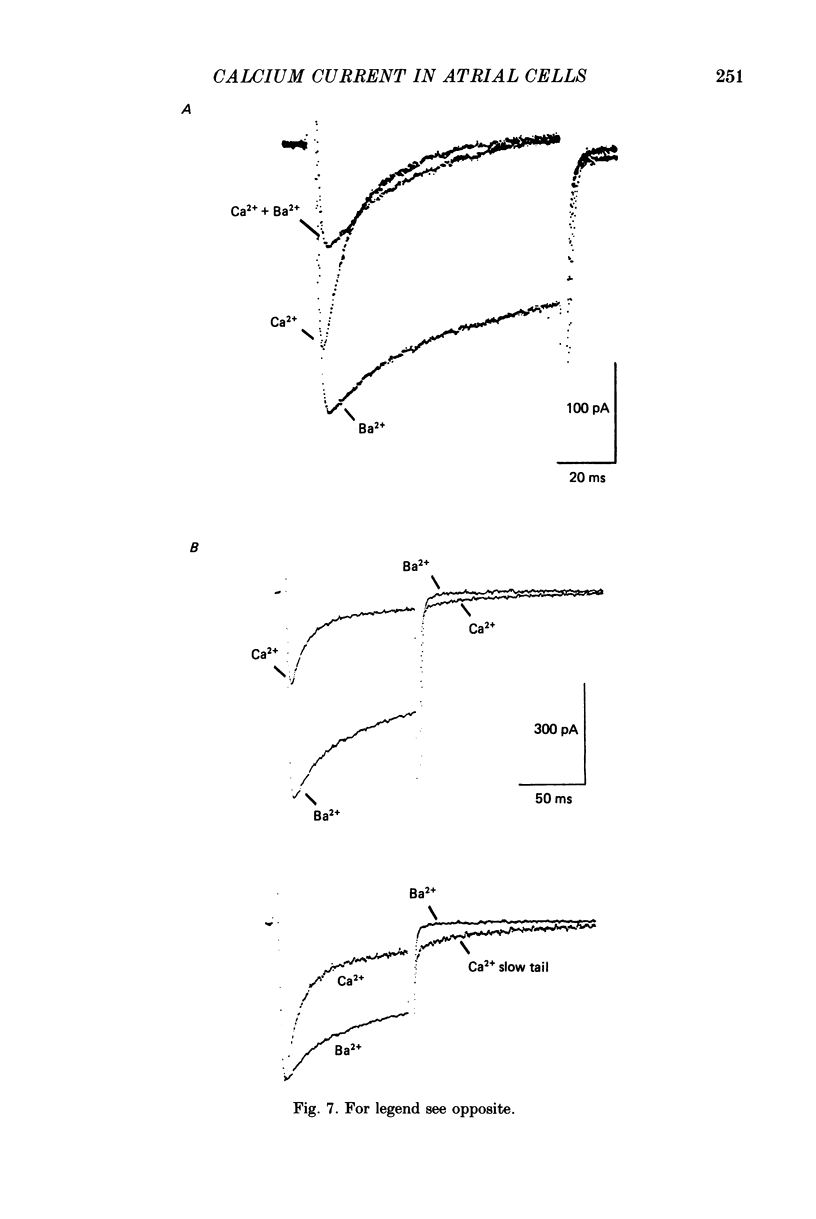
1. Voltage clamp studies on single cells from bull-frog atrium have been carried out to study the ion transfer characteristics of the calcium current, ICa. In agreement with the preliminary results of Hume & Giles (1983), a TTX-resistant, 'second transient inward current' was recorded consistently. Its average peak size at 0 mV in 2.5 mM [Ca2+]o Ringer solution was approximately -200 pA, and it was blocked by Cd2+ and La3+ but not by tetrodotoxin (TTX, 3 x 10(-6) M). 2. The peak size of this current increases by approximately 4 times when [Ca2+]o is raised from 1.25 to 7.5 mM, indicating that Ca2+ is a major charge carrier. 3. A well-defined reversal potential, Erev, for ICa can be recorded in normal Ringer solution and also when Ba2+ or Sr2+ serve as the charge carriers. When [Ca2+]o is changed the shifts in Erev follow the predictions of a Nernstian Ca2+ electrode. However, all Erev values are well below those predicted from the thermodynamic Nernstian ECa values (see Campbell, Giles, Hume, Noble & Shibata, 1988a). 4. The Ca2+ current exhibits voltage-dependent inactivation, whether the direction of net current flow is inward or outward; however, the rate of inactivation is affected by the species of cation carrying the current. Inactivation is reduced substantially in Ba2+ Ringer solution. 5. Magnesium (5 mM) is not a significant carrier or blocker of ICa in normal [Ca2+]o Ringer solution; however, 5 mM [Mg2+]o can block the current carried by either Sr2+ or Ba2+. In the absence of Mg2+, equimolar substitutions of Sr2+ or Ba2+ for Ca2+ result in larger currents than those carried by Ca2+ in the normal Ringer solution. 6. Sodium appears not to be a significant charge carrier in the presence of normal [Ca2+]o. However, after free [Ca2+]o has been reduced to extremely low levels (less than 10(-6) M) Na+ can carry a significant fraction of 'ICa'. Thus, it appears that the high selectivity of ICa for Ca2+ ions depends upon the presence of Ca2+. 7. 'Slow tails' are frequently recorded after repolarizing clamp steps back to the holding potential. These 'slow tails' are prominent in normal [Na+]o, [Ca2+]o and [Sr2+]o Ringer solution; however, they are markedly reduced in [Ba2+]o, in Na+-free and Ca2+-free Ringer solutions. Experimental and theoretical work suggests these slow tails may be generated by an electrogenic Na+-Ca2+ exchanger (see Campbell, Giles, Robinson & Shibata, 1988b).(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 400 WORDS)
Full text
PDF



















Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akaike N., Lee K. S., Brown A. M. The calcium current of Helix neuron. J Gen Physiol. 1978 May;71(5):509–531. doi: 10.1085/jgp.71.5.509. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Almers W., McCleskey E. W. Non-selective conductance in calcium channels of frog muscle: calcium selectivity in a single-file pore. J Physiol. 1984 Aug;353:585–608. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015352. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Almers W., McCleskey E. W., Palade P. T. A non-selective cation conductance in frog muscle membrane blocked by micromolar external calcium ions. J Physiol. 1984 Aug;353:565–583. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015351. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Attwell D., Cohen I. The voltage clamp of multicellular preparations. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 1977;31(3):201–245. doi: 10.1016/0079-6107(78)90009-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonvallet R. A low threshold calcium current recorded at physiological Ca concentrations in single frog atrial cells. Pflugers Arch. 1987 May;408(5):540–542. doi: 10.1007/BF00585084. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Byerly L., Chase P. B., Stimers J. R. Permeation and interaction of divalent cations in calcium channels of snail neurons. J Gen Physiol. 1985 Apr;85(4):491–518. doi: 10.1085/jgp.85.4.491. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Byerly L., Hagiwara S. Calcium currents in internally perfused nerve cell bodies of Limnea stagnalis. J Physiol. 1982 Jan;322:503–528. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014052. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell D. L., Giles W. R., Hume J. R., Noble D., Shibata E. F. Reversal potential of the calcium current in bull-frog atrial myocytes. J Physiol. 1988 Sep;403:267–286. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp017249. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell D. L., Giles W. R., Robinson K., Shibata E. F. Studies of the sodium-calcium exchanger in bull-frog atrial myocytes. J Physiol. 1988 Sep;403:317–340. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp017251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cavalié A., McDonald T. F., Pelzer D., Trautwein W. Temperature-induced transitory and steady-state changes in the calcium current of guinea pig ventricular myocytes. Pflugers Arch. 1985 Oct;405(3):294–296. doi: 10.1007/BF00582574. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chapman R. A. Excitation-contraction coupling in cardiac muscle. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 1979;35(1):1–52. doi: 10.1016/0079-6107(80)90002-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark R. B., Giles W. Sodium current in single cells from bullfrog atrium: voltage dependence and ion transfer properties. J Physiol. 1987 Oct;391:235–265. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016736. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colquhoun D., Neher E., Reuter H., Stevens C. F. Inward current channels activated by intracellular Ca in cultured cardiac cells. Nature. 1981 Dec 24;294(5843):752–754. doi: 10.1038/294752a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Connor J., Barr L., Jakobsson E. Electrical characteristics of frog atrial trabeculae in the double sucrose gap. Biophys J. 1975 Oct;15(10):1047–1067. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(75)85882-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durham A. C. A survey of readily available chelators for buffering calcium ion concentrations in physiological solutions. Cell Calcium. 1983 Feb;4(1):33–46. doi: 10.1016/0143-4160(83)90047-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRANKENHAEUSER B., HODGKIN A. L. The action of calcium on the electrical properties of squid axons. J Physiol. 1957 Jul 11;137(2):218–244. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1957.sp005808. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukushima Y., Hagiwara S. Currents carried by monovalent cations through calcium channels in mouse neoplastic B lymphocytes. J Physiol. 1985 Jan;358:255–284. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1985.sp015550. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giles W. R., Shibata E. F. Voltage clamp of bull-frog cardiac pace-maker cells: a quantitative analysis of potassium currents. J Physiol. 1985 Nov;368:265–292. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1985.sp015857. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagiwara S., Byerly L. Calcium channel. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1981;4:69–125. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.04.030181.000441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagiwara S., Jaffe L. A. Electrical properties of egg cell membranes. Annu Rev Biophys Bioeng. 1979;8:385–416. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.08.060179.002125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagiwara S., Nakajima S. Tetrodotoxin and manganese ion: effects on action potential of the frog heart. Science. 1965 Sep 10;149(3689):1254–1255. doi: 10.1126/science.149.3689.1254. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamill O. P., Marty A., Neher E., Sakmann B., Sigworth F. J. Improved patch-clamp techniques for high-resolution current recording from cells and cell-free membrane patches. Pflugers Arch. 1981 Aug;391(2):85–100. doi: 10.1007/BF00656997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hess P., Lansman J. B., Tsien R. W. Calcium channel selectivity for divalent and monovalent cations. Voltage and concentration dependence of single channel current in ventricular heart cells. J Gen Physiol. 1986 Sep;88(3):293–319. doi: 10.1085/jgp.88.3.293. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hess P., Tsien R. W. Mechanism of ion permeation through calcium channels. 1984 May 31-Jun 6Nature. 309(5967):453–456. doi: 10.1038/309453a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hille B. Charges and potentials at the nerve surface. Divalent ions and pH. J Gen Physiol. 1968 Feb;51(2):221–236. doi: 10.1085/jgp.51.2.221. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hille B., Schwarz W. Potassium channels as multi-ion single-file pores. J Gen Physiol. 1978 Oct;72(4):409–442. doi: 10.1085/jgp.72.4.409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horackova M., Vassort G. Sodium-calcium exchange in regulation of cardiac contractility. Evidence for an electrogenic, voltage-dependent mechanism. J Gen Physiol. 1979 Apr;73(4):403–424. doi: 10.1085/jgp.73.4.403. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hume J. R. Component of whole cell Ca current due to electrogenic Na-Ca-exchange in cardiac myocytes. Am J Physiol. 1987 Mar;252(3 Pt 2):H666–H670. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1987.252.3.H666. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hume J. R., Giles W. Ionic currents in single isolated bullfrog atrial cells. J Gen Physiol. 1983 Feb;81(2):153–194. doi: 10.1085/jgp.81.2.153. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hume J. R., Giles W., Robinson K., Shibata E. F., Nathan R. D., Kanai K., Rasmusson R. A time- and voltage-dependent K+ current in single cardiac cells from bullfrog atrium. J Gen Physiol. 1986 Dec;88(6):777–798. doi: 10.1085/jgp.88.6.777. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hume J. R., Uehara A. "Creep currents" in single frog atrial cells may be generated by electrogenic Na/Ca exchange. J Gen Physiol. 1986 Jun;87(6):857–884. doi: 10.1085/jgp.87.6.857. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isenberg G., Klöckner U. Calcium currents of isolated bovine ventricular myocytes are fast and of large amplitude. Pflugers Arch. 1982 Oct;395(1):30–41. doi: 10.1007/BF00584965. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson E. A., Lieberman M. Heart: excitation and contraction. Annu Rev Physiol. 1971;33:479–532. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.33.030171.002403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Josephson I. R., Sanchez-Chapula J., Brown A. M. A comparison of calcium currents in rat and guinea pig single ventricular cells. Circ Res. 1984 Feb;54(2):144–156. doi: 10.1161/01.res.54.2.144. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kass R. S., Krafte D. S. Negative surface charge density near heart calcium channels. Relevance to block by dihydropyridines. J Gen Physiol. 1987 Apr;89(4):629–644. doi: 10.1085/jgp.89.4.629. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kass R. S., Siegelbaum S. A., Tsien R. W. Three-micro-electrode voltage clamp experiments in calf cardiac Purkinje fibres: is slow inward current adequately measured? J Physiol. 1979 May;290(2):201–225. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1979.sp012768. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kostyuk P. G. Calcium channels in the neuronal membrane. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Dec;650(2-3):128–150. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(81)90003-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kostyuk P. G. Calcium ionic channels in electrically excitable membrane. Neuroscience. 1980;5(6):945–959. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(80)90178-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kostyuk P. G., Krishtal O. A. Effects of calcium and calcium-chelating agents on the inward and outward current in the membrane of mollusc neurones. J Physiol. 1977 Sep;270(3):569–580. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lammel E. A theoretical study on the sucrose gap technique as applied to multicellular muscle preparations. I. Saline-sucrose interdiffusion. Biophys J. 1981 Dec;36(3):533–553. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(81)84751-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lansman J. B., Hess P., Tsien R. W. Blockade of current through single calcium channels by Cd2+, Mg2+, and Ca2+. Voltage and concentration dependence of calcium entry into the pore. J Gen Physiol. 1986 Sep;88(3):321–347. doi: 10.1085/jgp.88.3.321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee K. S., Tsien R. W. High selectivity of calcium channels in single dialysed heart cells of the guinea-pig. J Physiol. 1984 Sep;354:253–272. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015374. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee K. S., Tsien R. W. Reversal of current through calcium channels in dialysed single heart cells. Nature. 1982 Jun 10;297(5866):498–501. doi: 10.1038/297498a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levi R., DeFelice L. J. Sodium-conducting channels in cardiac membranes in low calcium. Biophys J. 1986 Jul;50(1):5–9. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(86)83433-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuda H., Noma A. Isolation of calcium current and its sensitivity to monovalent cations in dialysed ventricular cells of guinea-pig. J Physiol. 1984 Dec;357:553–573. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015517. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonald T. F., Cavalié A., Trautwein W., Pelzer D. Voltage-dependent properties of macroscopic and elementary calcium channel currents in guinea pig ventricular myocytes. Pflugers Arch. 1986 May;406(5):437–448. doi: 10.1007/BF00583365. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonald T. F. The slow inward calcium current in the heart. Annu Rev Physiol. 1982;44:425–434. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.44.030182.002233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mentrard D., Vassort G., Fischmeister R. Calcium-mediated inactivation of the calcium conductance in cesium-loaded frog heart cells. J Gen Physiol. 1984 Jan;83(1):105–131. doi: 10.1085/jgp.83.1.105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mentrard D., Vassort G., Fischmeister R. Changes in external Na induce a membrane current related to the Na-Ca exchange in cesium-loaded frog heart cells. J Gen Physiol. 1984 Aug;84(2):201–220. doi: 10.1085/jgp.84.2.201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell M. R., Powell T., Terrar D. A., Twist V. W. Characteristics of the second inward current in cells isolated from rat ventricular muscle. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1983 Oct 22;219(1217):447–469. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1983.0084. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moisescu D. G. Kinetics of reaction in calcium-activated skinned muscle fibres. Nature. 1976 Aug 12;262(5569):610–613. doi: 10.1038/262610a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morad M., Goldman Y. E., Trentham D. R. Rapid photochemical inactivation of Ca2+-antagonists shows that Ca2+ entry directly activates contraction in frog heart. Nature. 1983 Aug 18;304(5927):635–638. doi: 10.1038/304635a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muller R. U., Finkelstein A. The electrostatic basis of Mg++ inhibition of transmitter release. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Mar;71(3):923–926. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.3.923. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mullins L. J. The generation of electric currents in cardiac fibers by Na/Ca exchange. Am J Physiol. 1979 Mar;236(3):C103–C110. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1979.236.3.C103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson M. T. Interactions of divalent cations with single calcium channels from rat brain synaptosomes. J Gen Physiol. 1986 Feb;87(2):201–222. doi: 10.1085/jgp.87.2.201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niedergerke R., Orkand R. K. The dual effect of calcium on the action potential of the frog's heart. J Physiol. 1966 May;184(2):291–311. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1966.sp007916. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Page S. G., Niedergerke R. Structures of physiological interest in the frog heart ventricle. J Cell Sci. 1972 Jul;11(1):179–203. doi: 10.1242/jcs.11.1.179. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Provencher S. W. A Fourier method for the analysis of exponential decay curves. Biophys J. 1976 Jan;16(1):27–41. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(76)85660-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reuter H. Divalent cations as charge carriers in excitable membranes. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 1973;26:1–43. doi: 10.1016/0079-6107(73)90016-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reuter H. Properties of two inward membrane currents in the heart. Annu Rev Physiol. 1979;41:413–424. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.41.030179.002213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson S. P., Johnson J. D., Potter J. D. The time-course of Ca2+ exchange with calmodulin, troponin, parvalbumin, and myosin in response to transient increases in Ca2+. Biophys J. 1981 Jun;34(3):559–569. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(81)84868-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson K., Giles W. A data acquisition, display and plotting program for the IBM PC. Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 1986 Dec;23(3):319–327. doi: 10.1016/0169-2607(86)90067-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rougier O., Vassort G., Garnier D., Gargouil Y. M., Coraboeuf E. Existence and role of a slow inward current during the frog atrial action potential. Pflugers Arch. 1969;308(2):91–110. doi: 10.1007/BF00587018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rougier O., Vassort G., Stämpfli R. Voltage clamp experiments on frog atrial heart muscle fibres with the sucrose gap technique. Pflugers Arch Gesamte Physiol Menschen Tiere. 1968;301(2):91–108. doi: 10.1007/BF00362729. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tarr M., Trank J. Equivalent circuit of frog atrial tissue as determined by voltage clamp-unclamp experiments. J Gen Physiol. 1971 Nov;58(5):511–522. doi: 10.1085/jgp.58.5.511. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tarr M. Two inward currents in frog atrial muscle. J Gen Physiol. 1971 Nov;58(5):523–543. doi: 10.1085/jgp.58.5.523. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsien R. W., Bean B. P., Hess P., Nowycky M. Calcium channels: mechanisms of beta-adrenergic modulation and ion permeation. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1983;48(Pt 1):201–212. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1983.048.01.023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsien R. W. Calcium channels in excitable cell membranes. Annu Rev Physiol. 1983;45:341–358. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.45.030183.002013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tung L., Morad M. A comparative electrophysiological study of enzymatically isolated single cells and strips of frog ventricle. Pflugers Arch. 1985 Oct;405(3):274–284. doi: 10.1007/BF00582572. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vassort G., Rougier O., Garnier D., Sauviat M. P., Coraboeuf E., Gargouïl Y. M. Effects of adrenaline on membrane inward currents during the cardiac action potential. Pflugers Arch. 1969;309(1):70–81. doi: 10.1007/BF00592283. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WRIGHT E. B., OGATA M. Action potential of amphibian single auricular muscle fiber: a dual response. Am J Physiol. 1961 Dec;201:1101–1108. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1961.201.6.1101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson D. L., Morimoto K., Tsuda Y., Brown A. M. Interaction between calcium ions and surface charge as it relates to calcium currents. J Membr Biol. 1983;72(1-2):117–130. doi: 10.1007/BF01870319. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto D., Washio H. Permeation of sodium through calcium channels of an insect muscle membrane. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1979 Feb;57(2):220–222. doi: 10.1139/y79-033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Hemptinne A. Voltage clamp analysis in isolated cardiac fibres as performed with two different perfusion chambres for double sucrose gap. Pflugers Arch. 1976 May 6;363(1):87–95. doi: 10.1007/BF00587407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


