Abstract
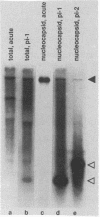
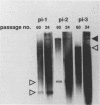
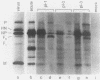
Three cell lines persistently infected with human parainfluenza virus type 3 were characterized on a molecular level in this study. All six structural protein genes were transcribed into monocistronic RNAs in the persistently infected cells. In both acutely and persistently infected cells, polycistronic transcripts were abundant, although the ratio of polycistronic to monocistronic transcripts was reduced in the persistently infected cells. Each of the persistently infected cell lines contained a distinct subgenomic RNA species. The subgenomic RNAs were present in purified nucleocapsid cores, indicating that they represent viral genome RNA, were far more abundant than full-length RNA, and were stably maintained through at least 36 cell passages. Nucleotide sequence analysis of the subgenomic RNAs from two of the persistently infected cell lines revealed that the 5' ends are identical to that of the standard genome. Hybridization experiments with oligonucleotide probes showed that both fragments retain sequences from the 5' end of the standard genome and contain approximately 1,200 nucleotides (cell line 1) and 1,500 nucleotides (cell line 2) of the polymerase gene sequence. The demonstration of several alterations in viral gene expression in persistently infected cells offers insight into the factors associated with persistence of parainfluenza virus 3.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Basle M. F., Russell W. C., Goswami K. K., Rebel A., Giraudon P., Wild F., Filmon R. Paramyxovirus antigens in osteoclasts from Paget's bone tissue detected by monoclonal antibodies. J Gen Virol. 1985 Oct;66(Pt 10):2103–2110. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-66-10-2103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cattaneo R., Rebmann G., Baczko K., ter Meulen V., Billeter M. A. Altered ratios of measles virus transcripts in diseased human brains. Virology. 1987 Oct;160(2):523–526. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90031-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cattaneo R., Schmid A., Rebmann G., Baczko K., Ter Meulen V., Bellini W. J., Rozenblatt S., Billeter M. A. Accumulated measles virus mutations in a case of subacute sclerosing panencephalitis: interrupted matrix protein reading frame and transcription alteration. Virology. 1986 Oct 15;154(1):97–107. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90433-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins P. L., Wertz G. W. cDNA cloning and transcriptional mapping of nine polyadenylylated RNAs encoded by the genome of human respiratory syncytial virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(11):3208–3212. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.11.3208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curran J. A., Quinn J. P., Hoey E. M., Martin S. J., Rima B. K. cDNA cloning of the nucleocapsid and nucleocapsid-associated protein genes of mumps virus. J Gen Virol. 1985 May;66(Pt 5):977–985. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-66-5-977. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De B. P., Galinski M. S., Banerjee A. K. Characterization of an in vitro system for the synthesis of mRNA from human parainfluenza virus type 3. J Virol. 1990 Mar;64(3):1135–1142. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.3.1135-1142.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galinski M. S., Mink M. A., Lambert D. M., Wechsler S. L., Pons M. W. Molecular cloning and sequence analysis of the human parainfluenza 3 virus RNA encoding the nucleocapsid protein. Virology. 1986 Mar;149(2):139–151. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90116-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galinski M. S., Mink M. A., Lambert D. M., Wechsler S. L., Pons M. W. Molecular cloning and sequence analysis of the human parainfluenza 3 virus gene encoding the matrix protein. Virology. 1987 Mar;157(1):24–30. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90309-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galinski M. S., Mink M. A., Lambert D. M., Wechsler S. L., Pons M. W. Molecular cloning and sequence analysis of the human parainfluenza 3 virus mRNA encoding the P and C proteins. Virology. 1986 Nov;155(1):46–60. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90167-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galinski M. S., Mink M. A., Pons M. W. Molecular cloning and sequence analysis of the human parainfluenza 3 virus gene encoding the L protein. Virology. 1988 Aug;165(2):499–510. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90594-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galinski M. S., Mink M. A., Pons M. W. Molecular cloning and sequence analysis of the human parainfluenza 3 virus genes encoding the surface glycoproteins, F and HN. Virus Res. 1987 Sep;8(3):205–215. doi: 10.1016/0168-1702(87)90016-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goswami K. K., Cameron K. R., Russell W. C., Lange L. S., Mitchell D. N. Evidence for the persistence of paramyxoviruses in human bone marrows. J Gen Virol. 1984 Nov;65(Pt 11):1881–1888. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-65-11-1881. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goswami K. K., Lange L. S., Mitchell D. N., Cameron K. R., Russell W. C. Does simian virus 5 infect humans? J Gen Virol. 1984 Aug;65(Pt 8):1295–1303. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-65-8-1295. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross P. A., Green R. H., Curnen M. G. Persistent infection with parainfluenza type 3 virus in man. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1973 Oct;108(4):894–898. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1973.108.4.894. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gupta K. C., Kingsbury D. W. Polytranscripts of Sendai virus do not contain intervening polyadenylate sequences. Virology. 1985 Feb;141(1):102–109. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(85)90186-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall W. W., Choppin P. W. Evidence for lack of synthesis of the M polypeptide of measles virus in brain cells in subacute sclerosing panencephalitis. Virology. 1979 Dec;99(2):443–447. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90026-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herman R. C., Schubert M., Keene J. D., Lazzarini R. A. Polycistronic vesicular stomatitis virus RNA transcripts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Aug;77(8):4662–4665. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.8.4662. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hodes D. S. Selection of temperature-sensitive mutants in persistent infection by parainfluenza virus type 3. J Gen Virol. 1982 Jun;60(Pt 2):401–404. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-60-2-401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holland J. J., Villarreal L. P., Welsh R. M., Oldstone M. B., Kohne D., Lazzarini R., Scolnick E. Long-term persistent vesicular stomatitis virus and rabies virus infection of cells in vitro. J Gen Virol. 1976 Nov;33(2):193–211. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-33-2-193. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang A. S., Baltimore D. Defective viral particles and viral disease processes. Nature. 1970 Apr 25;226(5243):325–327. doi: 10.1038/226325a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimura Y., Norrby E., Nagata I., Ito Y., Shimokata K. Homologous interference induced by a temperature-sensitive mutant derived from an HVJ (Sendai virus) carrier culture. J Gen Virol. 1976 Nov;33(2):333–343. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-33-2-333. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolakofsky D., Boy de la Tour E., Delius H. Molecular weight determination of Sendai and Newcastle disease virus RNA. J Virol. 1974 Feb;13(2):261–268. doi: 10.1128/jvi.13.2.261-268.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan E. M., Rapp F. Measles virus and its associated diseases. Bacteriol Rev. 1977 Sep;41(3):636–666. doi: 10.1128/br.41.3.636-666.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muchmore H. G., Parkinson A. J., Humphries J. E., Scott E. N., McIntosh D. A., Scott L. V., Cooney M. K., Miles J. A. Persistent parainfluenza virus shedding during isolation at the South Pole. Nature. 1981 Jan 15;289(5794):187–189. doi: 10.1038/289187a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy D. G., Dimock K., Kang C. Y. Defective interfering particles of human parainfluenza virus 3. Virology. 1987 Jun;158(2):439–443. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90217-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- P'ringle C. R., Shirodaria P. V., Cash P., Chiswell D. J., Malloy P. Initiation and maintenance of persistent infection by respiratory syncytial virus. J Virol. 1978 Oct;28(1):199–211. doi: 10.1128/jvi.28.1.199-211.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RAPP F. PLAQUE DIFFERENTIATION AND REPLICATION OF VIRULENT AND ATTENUATED STRAINS OF MEASLES VIRUS. J Bacteriol. 1964 Nov;88:1448–1458. doi: 10.1128/jb.88.5.1448-1458.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rima B. K., Davidson W. B., Martin S. J. The role of defective interfering particles in persistent infection of Vero cells by measles virus. J Gen Virol. 1977 Apr;35(1):89–97. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-35-1-89. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robbins S. J., Rapp F. Restriction of virus-specific protein synthesis in a persistent paramyxovirus infection. Arch Virol. 1982;71(1):85–91. doi: 10.1007/BF01315178. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roux L., Beffy P., Portner A. Restriction of cell surface expression of Sendai virus hemagglutinin-neuraminidase glycoprotein correlates with its higher instability in persistently and standard plus defective interfering virus infected BHK-21 cells. Virology. 1984 Oct 15;138(1):118–128. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90152-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roux L., Holland J. J. Role of defective interfering particles of Sendai virus in persistent infections. Virology. 1979 Feb;93(1):91–103. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90278-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roux L., Waldvogel F. A. Defective interfering particles of Sendai virus modulate HN expression at the surface of infected BHK cells. Virology. 1983 Oct 15;130(1):91–104. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90120-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roux L., Waldvogel F. A. Instability of the viral M protein in BHK-21 cells persistently infected with Sendai virus. Cell. 1982 Feb;28(2):293–302. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90347-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheid A., Choppin P. W. Protease activation mutants of sendai virus. Activation of biological properties by specific proteases. Virology. 1976 Jan;69(1):265–277. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(76)90213-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schloer G. M., Hanson R. P. Relationship of plaque size and virulence for chickens of 14 representative Newcastle disease virus strains. J Virol. 1968 Jan;2(1):40–47. doi: 10.1128/jvi.2.1.40-47.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sekellick M. J., Marcus P. I. Persistent infection. I Interferon-inducing defective-interfering particles as mediators of cell sparing: possible role in persistent infection by vesicular stomatitis virus. Virology. 1978 Mar;85(1):175–186. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(78)90422-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sekellick M. J., Marcus P. I. Persistent infection. II. Interferon-inducing temperature-sensitive mutants as mediators of cell sparing: possible role in persistent infection by vesicular stomatitis virus. Virology. 1979 May;95(1):36–47. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90399-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spriggs M. K., Collins P. L. Human parainfluenza virus type 3: messenger RNAs, polypeptide coding assignments, intergenic sequences, and genetic map. J Virol. 1986 Sep;59(3):646–654. doi: 10.1128/jvi.59.3.646-654.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thacore H., Youngner J. S. Cells persistently infected with newcastle disease virus: I. Properties of mutants isolated from persistently infected L cells. J Virol. 1969 Sep;4(3):244–251. doi: 10.1128/jvi.4.3.244-251.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuffereau C., Roux L. Direct adverse effects of Sendai virus DI particles on virus budding and on M protein fate and stability. Virology. 1988 Feb;162(2):417–426. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90482-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tyeryar F. J. Report of a workshop on respiratory syncytial virus and parainfluenza viruses. J Infect Dis. 1983 Sep;148(3):588–598. doi: 10.1093/infdis/148.3.588. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Udem S. A., Cook K. A. Isolation and characterization of measles virus intracellular nucleocapsid RNA. J Virol. 1984 Jan;49(1):57–65. doi: 10.1128/jvi.49.1.57-65.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WALKER D. L., HINZE H. C. A carrier state of mumps virus in human conjunctiva cells. I. General characteristics. J Exp Med. 1962 Nov 1;116:739–750. doi: 10.1084/jem.116.5.739. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wechsler S. L., Fields B. N. Intracellular synthesis of measles virus-specified polypeptides. J Virol. 1978 Jan;25(1):285–297. doi: 10.1128/jvi.25.1.285-297.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wechsler S. L., Lambert D. M., Galinski M. S., Heineke B. E., Pons M. W. Human parainfluenza virus 3: purification and characterization of subviral components, viral proteins and viral RNA. Virus Res. 1985 Nov;3(4):339–351. doi: 10.1016/0168-1702(85)90434-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wechsler S. L., Lambert D. M., Galinski M. S., Mink M. A., Rochovansky O., Pons M. W. Immediate persistent infection by human parainfluenza virus 3: unique fusion properties of the persistently infected cells. J Gen Virol. 1987 Jun;68(Pt 6):1737–1748. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-68-6-1737. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wechsler S. L., Lambert D. M., Galinski M. S., Pons M. W. Intracellular synthesis of human parainfluenza type 3 virus-specified polypeptides. J Virol. 1985 Jun;54(3):661–664. doi: 10.1128/jvi.54.3.661-664.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welliver R., Wong D. T., Choi T. S., Ogra P. L. Natural history of parainfluenza virus infection in childhood. J Pediatr. 1982 Aug;101(2):180–187. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(82)80113-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilde A., Morrison T. Structural and functional characterization of Newcastle disease virus polycistronic RNA species. J Virol. 1984 Jul;51(1):71–76. doi: 10.1128/jvi.51.1.71-76.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong T. C., Hirano A. Structure and function of bicistronic RNA encoding the phosphoprotein and matrix protein of measles virus. J Virol. 1987 Feb;61(2):584–589. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.2.584-589.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Youngner J. S., Dubovi E. J., Quagliana D. O., Kelly M., Preble O. T. Role of temperature-sensitive mutants in persistent infections initiated with vesicular stomatitis virus. J Virol. 1976 Jul;19(1):90–101. doi: 10.1128/jvi.19.1.90-101.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Youngner J. S., Jones E. V., Kelly M., Frielle D. W. Generation and amplification of temperature-sensitive mutants during serial undiluted passages of vesicular stomatitis virus. Virology. 1981 Jan 15;108(1):87–97. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90529-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]