Abstract
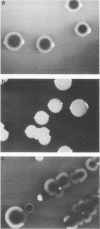
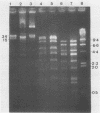
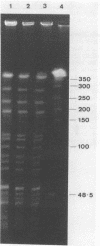
Two colonial variants of Staphylococcus epidermidis were isolated from the valvular tissue of a patient with native valve endocarditis. In addition to differing in colonial morphology, the two variants differed in hemolysis on blood-containing media, in adherence capacity, and in the expression of certain enzymes. Under suitable conditions, both variants were themselves capable of phenotypic variation, although they differed in the rate at which variants were generated. The variants yielded identical profiles on restriction endonuclease analysis of plasmid DNA and pulsed-field gel electrophoresis of whole-cell DNA. This report suggests a possible role for phenotypic variation in coagulase-negative staphylococcal virulence. Congo red agar would be an excellent medium for studying the contribution of variation to the virulence of these organisms.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baddour L. M., Barker L. P., Christensen G. D., Parisi J. T., Simpson W. A. Phenotypic variation of Staphylococcus epidermidis in infection of transvenous endocardial pacemaker electrodes. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Apr;28(4):676–679. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.4.676-679.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baddour L. M., Christensen G. D. Prosthetic valve endocarditis due to small-colony staphylococcal variants. Rev Infect Dis. 1987 Nov-Dec;9(6):1168–1174. doi: 10.1093/clinids/9.6.1168. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baddour L. M., Phillips T. N., Bisno A. L. Coagulase-negative staphylococcal endocarditis. Occurrence in patients with mitral valve prolapse. Arch Intern Med. 1986 Jan;146(1):119–121. doi: 10.1001/archinte.146.1.119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baddour L. M., Simpson W. A., Weems J. J., Jr, Hill M. M., Christensen G. D. Phenotypic selection of small-colony variant forms of Staphylococcus epidermidis in the rat model of endocarditis. J Infect Dis. 1988 Apr;157(4):757–763. doi: 10.1093/infdis/157.4.757. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borst P., Greaves D. R. Programmed gene rearrangements altering gene expression. Science. 1987 Feb 6;235(4789):658–667. doi: 10.1126/science.3544215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christensen G. D., Baddour L. M., Madison B. M., Parisi J. T., Abraham S. N., Hasty D. L., Lowrance J. H., Josephs J. A., Simpson W. A. Colonial morphology of staphylococci on Memphis agar: phase variation of slime production, resistance to beta-lactam antibiotics, and virulence. J Infect Dis. 1990 Jun;161(6):1153–1169. doi: 10.1093/infdis/161.6.1153. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christensen G. D., Simpson W. A., Bisno A. L., Beachey E. H. Adherence of slime-producing strains of Staphylococcus epidermidis to smooth surfaces. Infect Immun. 1982 Jul;37(1):318–326. doi: 10.1128/iai.37.1.318-326.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christensen G. D., Simpson W. A., Younger J. J., Baddour L. M., Barrett F. F., Melton D. M., Beachey E. H. Adherence of coagulase-negative staphylococci to plastic tissue culture plates: a quantitative model for the adherence of staphylococci to medical devices. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Dec;22(6):996–1006. doi: 10.1128/jcm.22.6.996-1006.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deighton M. A., Balkau B. Adherence measured by microtiter assay as a virulence marker for Staphylococcus epidermidis infections. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Nov;28(11):2442–2447. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.11.2442-2447.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fegan M., Francis P., Hayward A. C., Davis G. H., Fuerst J. A. Phenotypic conversion of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in cystic fibrosis. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Jun;28(6):1143–1146. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.6.1143-1146.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franklin J. C. Assessment of antibiotic-sensitive, intermediate or resistant status of bacteria by agar dilution. Med Lab Sci. 1988 Jul;45(3):225–234. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hébert G. A., Hancock G. A. Synergistic hemolysis exhibited by species of staphylococci. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Sep;22(3):409–415. doi: 10.1128/jcm.22.3.409-415.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lyon B. R., May J. W., Skurray R. A. Analysis of plasmids in nosocomial strains of multiple-antibiotic-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1983 Jun;23(6):817–826. doi: 10.1128/aac.23.6.817. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin M. A., Pfaller M. A., Massanari R. M., Wenzel R. P. Use of cellular hydrophobicity, slime production, and species identification markers for the clinical significance of coagulase-negative staphylococcal isolates. Am J Infect Control. 1989 Jun;17(3):130–135. doi: 10.1016/0196-6553(89)90199-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reifsteck F., Wee S., Wilkinson B. J. Hydrophobicity-hydrophilicity of staphylococci. J Med Microbiol. 1987 Aug;24(1):65–73. doi: 10.1099/00222615-24-1-65. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith C. L., Cantor C. R. Purification, specific fragmentation, and separation of large DNA molecules. Methods Enzymol. 1987;155:449–467. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)55030-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]