Abstract
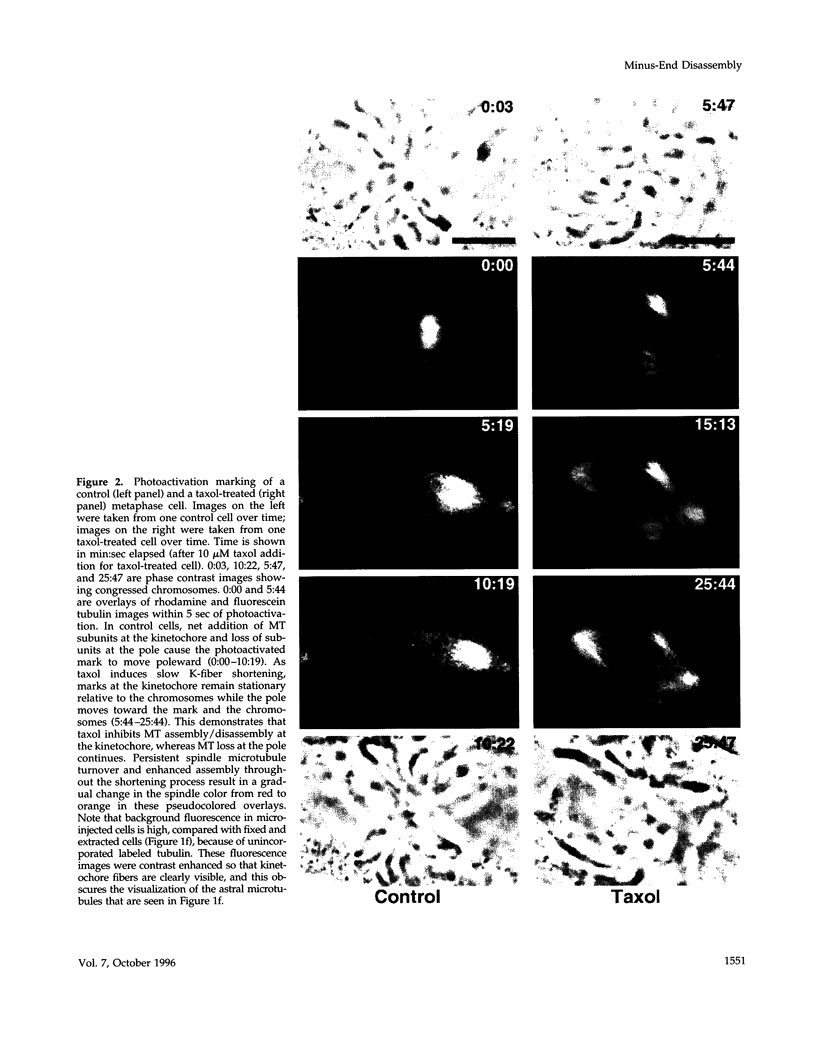
During metaphase and anaphase in newt lung cells, tubulin subunits within the kinetochore microtubule (kMT) lattice flux slowly poleward as kMTs depolymerize at their minus-ends within in the pole. Very little is known about how and where the force that moves the tubulin subunits poleward is generated and what function it serves during mitosis. We found that treatment with the drug taxol (10 microM) caused separated centrosomes in metaphase newt lung cells to move toward one another with an average velocity of 0.89 microns/min, until the interpolar distance was reduced by 22-62%. This taxol-induced spindle shortening occurred as kMTs between the chromosomes and the poles shortened. Photoactivation of fluorescent marks on kMTs revealed that taxol inhibited kinetochore microtubule assembly/disassembly at kinetochores, whereas minus-end MT disassembly continued at a rate typical of poleward flux in untreated metaphase cells. This poleward flux was strong enough to stretch the centromeric chromatin between sister kinetochores as much as it is stretched in control metaphase cells. In anaphase, taxol blocked kMT disassembly/assembly at the kinetochore whereas minus-end disassembly continued at a rate similar to flux in control cells (approximately 0.2 microns/min). These results reveal that the mechanism for kMT poleward flux 1) is not dependent on kMT plus-end dynamics and 2) produces pulling forces capable of generating tension across the centromeres of bioriented chromosomes.
Full text
PDF










Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ault J. G., DeMarco A. J., Salmon E. D., Rieder C. L. Studies on the ejection properties of asters: astral microtubule turnover influences the oscillatory behavior and positioning of mono-oriented chromosomes. J Cell Sci. 1991 Aug;99(Pt 4):701–710. doi: 10.1242/jcs.99.4.701. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ault J. G., Nicklas R. B. Tension, microtubule rearrangements, and the proper distribution of chromosomes in mitosis. Chromosoma. 1989 Jun;98(1):33–39. doi: 10.1007/BF00293332. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cassimeris L., Rieder C. L., Salmon E. D. Microtubule assembly and kinetochore directional instability in vertebrate monopolar spindles: implications for the mechanism of chromosome congression. J Cell Sci. 1994 Jan;107(Pt 1):285–297. doi: 10.1242/jcs.107.1.285. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cassimeris L., Salmon E. D. Kinetochore microtubules shorten by loss of subunits at the kinetochores of prometaphase chromosomes. J Cell Sci. 1991 Feb;98(Pt 2):151–158. doi: 10.1242/jcs.98.2.151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Centonze V. E., Borisy G. G. Pole-to-chromosome movements induced at metaphase: sites of microtubule disassembly. J Cell Sci. 1991 Sep;100(Pt 1):205–211. doi: 10.1242/jcs.100.1.205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cyert M. S., Scherson T., Kirschner M. W. Monoclonal antibodies specific for thiophosphorylated proteins recognize Xenopus MPF. Dev Biol. 1988 Sep;129(1):209–216. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(88)90175-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Brabander M., Geuens G., Nuydens R., Willebrords R., Aerts F., De Mey J. Microtubule dynamics during the cell cycle: the effects of taxol and nocodazole on the microtubule system of Pt K2 cells at different stages of the mitotic cycle. Int Rev Cytol. 1986;101:215–274. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)60250-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Derry W. B., Wilson L., Jordan M. A. Substoichiometric binding of taxol suppresses microtubule dynamics. Biochemistry. 1995 Feb 21;34(7):2203–2211. doi: 10.1021/bi00007a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desai A., Mitchison T. J. A new role for motor proteins as couplers to depolymerizing microtubules. J Cell Biol. 1995 Jan;128(1-2):1–4. doi: 10.1083/jcb.128.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Endow S. A., Chandra R., Komma D. J., Yamamoto A. H., Salmon E. D. Mutants of the Drosophila ncd microtubule motor protein cause centrosomal and spindle pole defects in mitosis. J Cell Sci. 1994 Apr;107(Pt 4):859–867. doi: 10.1242/jcs.107.4.859. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Endow S. A., Kang S. J., Satterwhite L. L., Rose M. D., Skeen V. P., Salmon E. D. Yeast Kar3 is a minus-end microtubule motor protein that destabilizes microtubules preferentially at the minus ends. EMBO J. 1994 Jun 1;13(11):2708–2713. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06561.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FORER A. LOCAL REDUCTION OF SPINDLE FIBER BIREFRINGENCE IN LIVING NEPHROTOMA SUTURALIS (LOEW) SPERMATOCYTES INDUCED BY ULTRAVIOLET MICROBEAM IRRADIATION. J Cell Biol. 1965 Apr;25:SUPPL–SUPPL117. doi: 10.1083/jcb.25.1.95. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forer A. Characterization of the mitotic traction system, and evidence that birefringent spindle fibers neither produce nor transmit force for chromosome movement. Chromosoma. 1966;19(1):44–98. doi: 10.1007/BF00332793. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuller M. T. Riding the polar winds: chromosomes motor down east. Cell. 1995 Apr 7;81(1):5–8. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90364-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaglio T., Saredi A., Compton D. A. NuMA is required for the organization of microtubules into aster-like mitotic arrays. J Cell Biol. 1995 Nov;131(3):693–708. doi: 10.1083/jcb.131.3.693. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorbsky G. J. Kinetochores, microtubules and the metaphase checkpoint. Trends Cell Biol. 1995 Apr;5(4):143–148. doi: 10.1016/s0962-8924(00)88968-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorbsky G. J., Ricketts W. A. Differential expression of a phosphoepitope at the kinetochores of moving chromosomes. J Cell Biol. 1993 Sep;122(6):1311–1321. doi: 10.1083/jcb.122.6.1311. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorbsky G. J., Sammak P. J., Borisy G. G. Chromosomes move poleward in anaphase along stationary microtubules that coordinately disassemble from their kinetochore ends. J Cell Biol. 1987 Jan;104(1):9–18. doi: 10.1083/jcb.104.1.9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hays T. S., Salmon E. D. Poleward force at the kinetochore in metaphase depends on the number of kinetochore microtubules. J Cell Biol. 1990 Feb;110(2):391–404. doi: 10.1083/jcb.110.2.391. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inoué S., Salmon E. D. Force generation by microtubule assembly/disassembly in mitosis and related movements. Mol Biol Cell. 1995 Dec;6(12):1619–1640. doi: 10.1091/mbc.6.12.1619. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jordan M. A., Toso R. J., Thrower D., Wilson L. Mechanism of mitotic block and inhibition of cell proliferation by taxol at low concentrations. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Oct 15;90(20):9552–9556. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.20.9552. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maekawa T., Leslie R., Kuriyama R. Identification of a minus end-specific microtubule-associated protein located at the mitotic poles in cultured mammalian cells. Eur J Cell Biol. 1991 Apr;54(2):255–267. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margolis R. L., Wilson L. Microtubule treadmills--possible molecular machinery. Nature. 1981 Oct 29;293(5835):705–711. doi: 10.1038/293705a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McIntosh J. R. Structural and mechanical control of mitotic progression. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1991;56:613–619. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1991.056.01.070. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McNally F. J., Vale R. D. Identification of katanin, an ATPase that severs and disassembles stable microtubules. Cell. 1993 Nov 5;75(3):419–429. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90377-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McNeill P. A., Berns M. W. Chromosome behavior after laser microirradiation of a single kinetochore in mitotic PtK2 cells. J Cell Biol. 1981 Mar;88(3):543–553. doi: 10.1083/jcb.88.3.543. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchison T. J. Polewards microtubule flux in the mitotic spindle: evidence from photoactivation of fluorescence. J Cell Biol. 1989 Aug;109(2):637–652. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.2.637. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchison T. J., Salmon E. D. Poleward kinetochore fiber movement occurs during both metaphase and anaphase-A in newt lung cell mitosis. J Cell Biol. 1992 Nov;119(3):569–582. doi: 10.1083/jcb.119.3.569. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchison T. J., Sawin K. E. Tubulin flux in the mitotic spindle: where does it come from, where is it going? Cell Motil Cytoskeleton. 1990;16(2):93–98. doi: 10.1002/cm.970160202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moritz M., Braunfeld M. B., Sedat J. W., Alberts B., Agard D. A. Microtubule nucleation by gamma-tubulin-containing rings in the centrosome. Nature. 1995 Dec 7;378(6557):638–640. doi: 10.1038/378638a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicklas R. B., Koch C. A. Chromosome micromanipulation. 3. Spindle fiber tension and the reorientation of mal-oriented chromosomes. J Cell Biol. 1969 Oct;43(1):40–50. doi: 10.1083/jcb.43.1.40. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rieder C. L., Alexander S. P. Kinetochores are transported poleward along a single astral microtubule during chromosome attachment to the spindle in newt lung cells. J Cell Biol. 1990 Jan;110(1):81–95. doi: 10.1083/jcb.110.1.81. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rieder C. L., Davison E. A., Jensen L. C., Cassimeris L., Salmon E. D. Oscillatory movements of monooriented chromosomes and their position relative to the spindle pole result from the ejection properties of the aster and half-spindle. J Cell Biol. 1986 Aug;103(2):581–591. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.2.581. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rieder C. L., Hard R. Newt lung epithelial cells: cultivation, use, and advantages for biomedical research. Int Rev Cytol. 1990;122:153–220. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)61208-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rieder C. L., Salmon E. D. Motile kinetochores and polar ejection forces dictate chromosome position on the vertebrate mitotic spindle. J Cell Biol. 1994 Feb;124(3):223–233. doi: 10.1083/jcb.124.3.223. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rieder C. L., Schultz A., Cole R., Sluder G. Anaphase onset in vertebrate somatic cells is controlled by a checkpoint that monitors sister kinetochore attachment to the spindle. J Cell Biol. 1994 Dec;127(5):1301–1310. doi: 10.1083/jcb.127.5.1301. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salmon E. D., Inoué T., Desai A., Murray A. W. High resolution multimode digital imaging system for mitosis studies in vivo and in vitro. Biol Bull. 1994 Oct;187(2):231–232. doi: 10.1086/BBLv187n2p231. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawin K. E., Mitchison T. J. Microtubule flux in mitosis is independent of chromosomes, centrosomes, and antiparallel microtubules. Mol Biol Cell. 1994 Feb;5(2):217–226. doi: 10.1091/mbc.5.2.217. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawin K. E., Mitchison T. J. Poleward microtubule flux mitotic spindles assembled in vitro. J Cell Biol. 1991 Mar;112(5):941–954. doi: 10.1083/jcb.112.5.941. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiff P. B., Horwitz S. B. Taxol stabilizes microtubules in mouse fibroblast cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Mar;77(3):1561–1565. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.3.1561. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skibbens R. V., Rieder C. L., Salmon E. D. Kinetochore motility after severing between sister centromeres using laser microsurgery: evidence that kinetochore directional instability and position is regulated by tension. J Cell Sci. 1995 Jul;108(Pt 7):2537–2548. doi: 10.1242/jcs.108.7.2537. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skibbens R. V., Skeen V. P., Salmon E. D. Directional instability of kinetochore motility during chromosome congression and segregation in mitotic newt lung cells: a push-pull mechanism. J Cell Biol. 1993 Aug;122(4):859–875. doi: 10.1083/jcb.122.4.859. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vernos I., Karsenti E. Motors involved in spindle assembly and chromosome segregation. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1996 Feb;8(1):4–9. doi: 10.1016/s0955-0674(96)80041-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waters J. C., Cole R. W., Rieder C. L. The force-producing mechanism for centrosome separation during spindle formation in vertebrates is intrinsic to each aster. J Cell Biol. 1993 Jul;122(2):361–372. doi: 10.1083/jcb.122.2.361. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wells W. A. The spindle-assembly checkpoint: aiming for a perfect mitosis, every time. Trends Cell Biol. 1996 Jun;6(6):228–234. doi: 10.1016/0962-8924(96)10018-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson P. J., Forer A., Leggiadro C. Evidence that kinetochore microtubules in crane-fly spermatocytes disassemble during anaphase primarily at the poleward end. J Cell Sci. 1994 Nov;107(Pt 11):3015–3027. doi: 10.1242/jcs.107.11.3015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhai Y., Kronebusch P. J., Borisy G. G. Kinetochore microtubule dynamics and the metaphase-anaphase transition. J Cell Biol. 1995 Nov;131(3):721–734. doi: 10.1083/jcb.131.3.721. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zheng Y., Wong M. L., Alberts B., Mitchison T. Nucleation of microtubule assembly by a gamma-tubulin-containing ring complex. Nature. 1995 Dec 7;378(6557):578–583. doi: 10.1038/378578a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]