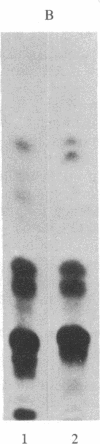
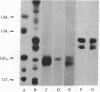
Abstract
The predominant gangliosides produced by two cultured human melanoma cell lines are GD3 and/or GD2. These gangliosides were found to be cell associated and present in substratum-attached material after cell removal by EDTA. Monoclonal antibodies directed to GD2 and GD3 specified the cell-surface distribution of these gangliosides and localized them in focal adhesion plaques at the interface of cells and their substratum. These attachment sites did not represent indiscriminant membrane fragments remaining after removal of cells with EDTA, because neither melanoma-associated proteoglycan nor class I histocompatibility antigens were detected by their respective antibodies. Our data suggest that the disialogangliosides GD2 and GD3 may be involved in the interaction between human melanoma cells and solid substrata.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albino A. P., Lloyd K. O., Ikeda H., Old L. J. Biochemical analysis of a 130,000 molecular weight glycoprotein on human melanoma cells. J Immunol. 1983 Sep;131(3):1595–1599. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackburn C. C., Schnaar R. L. Carbohydrate-specific cell adhesion is mediated by immobilized glycolipids. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jan 25;258(2):1180–1188. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown J. P., Hewick R. M., Hellström I., Hellström K. E., Doolittle R. F., Dreyer W. J. Human melanoma-associated antigen p97 is structurally and functionally related to transferrin. Nature. 1982 Mar 11;296(5853):171–173. doi: 10.1038/296171a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bumol T. F., Reisfeld R. A. Biosynthesis and secretion of fibronectin in human melanoma cells. J Cell Biochem. 1983;21(2):129–140. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240210204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bumol T. F., Reisfeld R. A. Unique glycoprotein-proteoglycan complex defined by monoclonal antibody on human melanoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Feb;79(4):1245–1249. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.4.1245. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butters T. D., Devalia V., Aplin J. D., Hughes R. C. Inhibition of fibronectin-mediated adhesion of hamster fibroblasts to substratum: effects of tunicamycin and some cell surface modifying reagents. J Cell Sci. 1980 Aug;44:33–58. doi: 10.1242/jcs.44.1.33. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cahan L. D., Irie R. F., Singh R., Cassidenti A., Paulson J. C. Identification of a human neuroectodermal tumor antigen (OFA-I-2) as ganglioside GD2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(24):7629–7633. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.24.7629. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheresh D. A., Varki A. P., Varki N. M., Stallcup W. B., Levine J., Reisfeld R. A. A monoclonal antibody recognizes an O-acylated sialic acid in a human melanoma-associated ganglioside. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jun 25;259(12):7453–7459. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Culp L. A., Black P. H. Release of macromolecules from BALB-c mouse cell lines treated with chelating agents. Biochemistry. 1972 May 23;11(11):2161–2172. doi: 10.1021/bi00761a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dippold W. G., Knuth A., Meyer zum Büschenfelde K. H. Inhibition of human melanoma cell growth in vitro by monoclonal anti-GD3-ganglioside antibody. Cancer Res. 1984 Feb;44(2):806–810. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenbarth G. S., Walsh F. S., Nirenberg M. Monoclonal antibody to a plasma membrane antigen of neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):4913–4917. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.4913. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hakomori S., Kannagi R. Glycosphingolipids as tumor-associated and differentiation markers. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1983 Aug;71(2):231–251. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harper J. R., Bumol T. F., Reisfeld R. A. Characterization of monoclonal antibody 155.8 and partial characterization of its proteoglycan antigen on human melanoma cells. J Immunol. 1984 Apr;132(4):2096–2104. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harper J. R., Bumol T. F., Reisfeld R. A. Serological and biochemical analyses of monoclonal antibodies to human melanoma-associated antigens. Hybridoma. 1982;1(4):423–432. doi: 10.1089/hyb.1.1982.1.423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jourdian G. W., Dean L., Roseman S. The sialic acids. XI. A periodate-resorcinol method for the quantitative estimation of free sialic acids and their glycosides. J Biol Chem. 1971 Jan 25;246(2):430–435. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kato I., Naiki M. Ganglioside and rabbit erythrocyte membrane receptor for staphylococcal alpha-toxin. Infect Immun. 1976 Jan;13(1):289–291. doi: 10.1128/iai.13.1.289-291.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koprowski H., Steplewski Z., Mitchell K., Herlyn M., Herlyn D., Fuhrer P. Colorectal carcinoma antigens detected by hybridoma antibodies. Somatic Cell Genet. 1979 Nov;5(6):957–971. doi: 10.1007/BF01542654. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ledeen R. W., Yu R. K. Gangliosides: structure, isolation, and analysis. Methods Enzymol. 1982;83:139–191. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(82)83012-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magnani J. L., Smith D. F., Ginsburg V. Detection of gangliosides that bind cholera toxin: direct binding of 125I-labeled toxin to thin-layer chromatograms. Anal Biochem. 1980 Dec;109(2):399–402. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90667-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nudelman E., Hakomori S., Kannagi R., Levery S., Yeh M. Y., Hellström K. E., Hellström I. Characterization of a human melanoma-associated ganglioside antigen defined by a monoclonal antibody, 4.2. J Biol Chem. 1982 Nov 10;257(21):12752–12756. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perkins R. M., Kellie S., Patel B., Critchley D. R. Gangliosides as receptors for fibronectin? Comparison of cell spreading on a ganglioside-specific ligand with that on fibronectin. Exp Cell Res. 1982 Oct;141(2):231–243. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(82)90211-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pukel C. S., Lloyd K. O., Travassos L. R., Dippold W. G., Oettgen H. F., Old L. J. GD3, a prominent ganglioside of human melanoma. Detection and characterisation by mouse monoclonal antibody. J Exp Med. 1982 Apr 1;155(4):1133–1147. doi: 10.1084/jem.155.4.1133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rohrschneider L. R. Adhesion plaques of Rous sarcoma virus-transformed cells contain the src gene product. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jun;77(6):3514–3518. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.6.3514. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SVENNERHOLM L. CHROMATOGRAPHIC SEPARATION OF HUMAN BRAIN GANGLIOSIDES. J Neurochem. 1963 Sep;10:613–623. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1963.tb08933.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varki N. M., Reisfeld R. A., Walker L. E. Antigens associated with a human lung adenocarcinoma defined by monoclonal antibodies. Cancer Res. 1984 Feb;44(2):681–687. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yogeeswaran G. Incorporation of asialo GM2 and gangliosides in cell surface of cultured metastatic and nonmetastatic BALB/3T3 cell lines: subcutaneous tumor cell take. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1981 Feb;66(2):303–310. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]